Effects of recombinant human interleukin 7 on T-cell recovery and thymic output in HIV-infected patients receiving antiretroviral therapy: results of a phase I/IIa randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter study
- PMID: 22550117
- PMCID: PMC3381639
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/cis383
Effects of recombinant human interleukin 7 on T-cell recovery and thymic output in HIV-infected patients receiving antiretroviral therapy: results of a phase I/IIa randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter study
Abstract
Background: The immune deficiency of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection is not fully corrected with ARV therapy. Interleukin-7 (IL-7) can boost CD4 T-cell counts, but optimal dosing and mechanisms of cellular increases need to be defined.
Methods: We performed a randomized placebo-controlled dose escalation (10, 20 and 30 µg/kg) trial of 3 weekly doses of recombinant human IL-7 (rhIL-7) in ARV-treated HIV-infected persons with CD4 T-cell counts between 101 and 400 cells/µL and plasma HIV levels <50 copies/mL. Toxicity, activity and the impact of rhIL-7 on immune reconstitution were monitored.
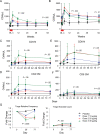
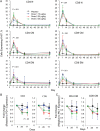
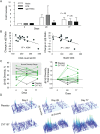
Results: Doses of rhIL-7 up to 20 µg/kg were well tolerated. CD4 increases of predominantly naive and central memory T cells were brisk (averaging 323 cells/µL at 12 weeks) and durable (up to 1 year). Increased cell cycling and transient increased bcl-2 expression were noted. Expanded cells did not have the characteristics of regulatory or activated T cells. Transient low-level HIV viremia was seen in 6 of 26 treated patients; modest increases in total levels of intracellular HIV DNA were proportional to CD4 T-cell expansions. IL-7 seemed to increase thymic output and tended to improve the T-cell receptor (TCR) repertoire in persons with low TCR diversity.
Conclusions: Three weekly doses of rhIL-7 at 20 µg/kg are well tolerated and lead to a dose-dependent CD4 T-cell increase and the broadening of TCR diversity in some subjects. These data suggest that this rhIL-7 dose could be advanced in future rhIL-7 clinical studies.
Clinical trials registration: NCT0047732.
Figures
References
-
- Beq S, Delfraissy JF, Theze J. Interleukin-7 (IL-7): immune function, involvement in the pathogenesis of HIV infection and therapeutic potential. Euro Cytokine Netw. 2004;15:279–89. - PubMed
-
- Puel A, Ziegler SF, Buckley RH, Leonard WJ. Defective IL7R expression in T-B+NK+ severe combined immunodeficiency. Nat Gene. 1998;20:394–7. - PubMed
-
- Noguchi M, Nakamura Y, Russell SM, et al. Interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain: a functional component of the interleukin-7 receptor. Science. 1993;262:1877–80. - PubMed
-
- Bolotin E, Annett G, Parkman R, Weinberg K. Serum levels of IL-7 in bone marrow transplant recipients: relationship to clinical characteristics and lymphocyte count. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1999;23:783–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

