Effects of belimumab, a B lymphocyte stimulator-specific inhibitor, on disease activity across multiple organ domains in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: combined results from two phase III trials
- PMID: 22550315
- PMCID: PMC3465857
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200831
Effects of belimumab, a B lymphocyte stimulator-specific inhibitor, on disease activity across multiple organ domains in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: combined results from two phase III trials
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effects of belimumab versus placebo, plus standard systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) therapy, on organ domain-specific SLE disease activity.
Methods: Data obtained after 52 weeks of treatment from two phase III trials (BLISS-52 and BLISS-76) comparing belimumab 1 and 10 mg/kg versus placebo, plus standard therapy, in 1684 autoantibody-positive patients were analysed post hoc for changes in British Isles Lupus Assessment Group (BILAG) and Safety of Estrogens in Lupus National Assessment-Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SELENA-SLEDAI) organ domain scores.
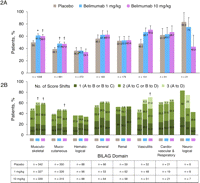
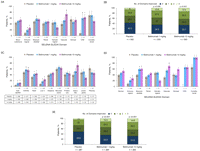
Results: At baseline, the domains involved in the majority of patients were musculoskeletal and mucocutaneous by both BILAG and SELENA-SLEDAI, and immunological by SELENA-SLEDAI. At 52 weeks, significantly more patients treated with belimumab versus placebo had improvement in BILAG musculoskeletal and mucocutaneous domains (1 and 10 mg/kg), and in SELENA-SLEDAI mucocutaneous (10 mg/kg), musculoskeletal (1 mg/kg) and immunological (1 and 10 mg/kg) domains. Improvement was also observed in other organ systems with a low prevalence (≤16%) at baseline, including the SELENA-SLEDAI vasculitis and central nervous system domains. Significantly fewer patients treated with belimumab versus placebo had worsening in the BILAG haematological domain (1 mg/kg) and in the SELENA-SLEDAI immunological (10 mg/kg), haematological (10 mg/kg) and renal (1 mg/kg) domains.
Conclusions: Belimumab treatment improved overall SLE disease activity in the most common musculoskeletal and mucocutaneous organ domains. Less worsening occurred in the haematological, immunological and renal domains.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Lau CS, Mak A. The socioeconomic burden of SLE. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2009;5:400–4 - PubMed
-
- Rahman A, Isenberg DA. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 2008;358:929–39 - PubMed
-
- Baker KP, Edwards BM, Main SH, et al. Generation and characterization of LymphoStat-B, a human monoclonal antibody that antagonizes the bioactivities of B lymphocyte stimulator. Arthritis Rheum 2003;48:3253–65 - PubMed
-
- Petri M, Stohl W, Chatham W, et al. Association of plasma B lymphocyte stimulator levels and disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2008;58:2453–9 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

