Correction of coagulopathy for percutaneous interventions
- PMID: 22550375
- PMCID: PMC3324201
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0030-1267857
Correction of coagulopathy for percutaneous interventions
Abstract
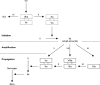
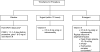
Due to medical illness or pharmacotherapy, patients undergoing percutaneous interventions often have abnormal hemostasis. Its etiology may include alterations in the protein-based coagulation system, thrombocytopenia, deficient platelet function, or mixed deficits such as disseminated intravascular coagulation. In this article, the authors review the basic science of each of these etiologies, as well as their available methods of correction. They also review the evidence and guidelines regarding the assessment and treatment of coagulopathy in image-guided procedures. The periprocedural bleeding risk and the urgency of a given procedure guide the management of abnormal hemostasis in this patient population.
Keywords: Anticoagulation; coagulopathy; disseminated intravascular coagulation; platelets; reversal.
Figures
References
-
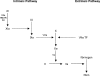
- Davie E W, Ratnoff O D. Waterfall sequence for intrinsic blood clotting. Science. 1964;145:1310–1312. - PubMed
-
- MacFarlane R G. An enzyme cascade in the blood clotting mechanism, and its function as a biological amplifier. Nature. 1964;202:498–499. - PubMed
-
- Hoffman M, Monroe D M., III A cell-based model of hemostasis. Thromb Haemost. 2001;85(6):958–965. - PubMed
-
- Douketis J D, Berger P B, Dunn A S, Jaffer A K, Spyropoulos A C, Becker R C. Ansell. The perioperative management of antithrombotic therapy. Chest. 2008;133:299S–339S. - PubMed
-
- White R H, McKittrick T, Hutchinson R, Twitchell J. Temporary discontinuation of warfarin therapy: changes in the international normalized ratio. Ann Intern Med. 1995;122(1):40–42. - PubMed

