Characteristics of disease spectrum in relation to species, serogroups, and adhesion ability of motile aeromonads in fish
- PMID: 22550470
- PMCID: PMC3322513
- DOI: 10.1100/2012/949358
Characteristics of disease spectrum in relation to species, serogroups, and adhesion ability of motile aeromonads in fish
Abstract
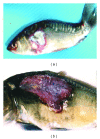
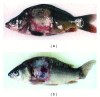
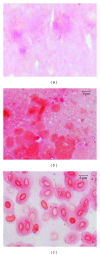
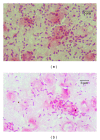
An attempt was made to delineate the relationship between of Aeromonas species and/or serogroups and specific disease symptoms in common carp Cyprinus carpio L. and rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum. The adhesion of Aeromonas strains to various tissues in relation to disease spectrum was also tested. All strains of A. hydrophila caused skin ulcers as well as septicaemia in both carp and trout while the other strains were able to cause only skin ulcers or some specific internal lesions with or without septicaemia depending on which species and/or serogroup they represented. Disease symptoms depended also on fish species. It was found that adhesion intensity of Aeromonas strains tested was significantly higher to tissues, which were susceptible to infection with these strains. The results indicate that adhesion to various cells of the fish organism is principal marker to detect virulent Aeromonas strains. The findings presented in this study may be helpful in the appraisal of aeromonads disease risk and kind of the infection in particular fish farms by epizootiological studies or/and during routine fish examinations. They will also be useful to improve and facilitate diagnosis of bacterial fish disease.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Immunochemical studies and gene cluster relationships of closely related O-antigens of Aeromonas hydrophila Pt679, Aeromonas popoffii A4, and Aeromonas sobria K928 strains classified into the PGO1 serogroup dominant in Polish aquaculture of carp and rainbow trout.Carbohydr Res. 2023 Sep;531:108896. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2023.108896. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Carbohydr Res. 2023. PMID: 37437416
-
Recovery of Bacillus mycoides, B. pseudomycoides and Aeromonas hydrophila from common carp (Cyprinus carpio) and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) with gill disease.J Fish Dis. 2018 Jan;41(1):125-129. doi: 10.1111/jfd.12686. Epub 2017 Jul 26. J Fish Dis. 2018. PMID: 28745820
-
Mesophilic aeromonads in wild and aquacultured freshwater fish.J Food Prot. 2001 May;64(5):687-91. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-64.5.687. J Food Prot. 2001. PMID: 11348001
-
Occurrence and significance of atypical Aeromonas salmonicida in non-salmonid and salmonid fish species: a review.Dis Aquat Organ. 1998 Feb 26;32(1):49-69. doi: 10.3354/dao032049. Dis Aquat Organ. 1998. PMID: 9696626 Review.
-
Aeromonas flagella and colonisation mechanisms.Adv Microb Physiol. 2014;65:203-56. doi: 10.1016/bs.ampbs.2014.08.007. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Adv Microb Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25476767 Review.
Cited by
-
Microbiological analysis of skin lesions of cod (Gadus morhua) from the southern part of the Baltic Sea.J Vet Res. 2024 Mar 23;68(1):79-92. doi: 10.2478/jvetres-2024-0004. eCollection 2024 Mar. J Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38525229 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Role of microRNAs in Response to Aeromonas Infection in Fish.Arch Razi Inst. 2023 Dec 30;78(6):1668-1679. doi: 10.32592/ARI.2023.78.6.1668. eCollection 2023 Dec. Arch Razi Inst. 2023. PMID: 38828176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Screening of the Protective Antigens of Aeromonas hydrophila Using the Reverse Vaccinology Approach: Potential Candidates for Subunit Vaccine Development.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jul 21;11(7):1266. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11071266. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37515081 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of an actin-targeting ADP-ribosyltransferase from Aeromonas hydrophila.J Biol Chem. 2012 Oct 26;287(44):37030-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.397612. Epub 2012 Sep 11. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22969084 Free PMC article.
-
Draft Genome Sequence of Aeromonas hydrophila Strain BSK-10 (Serotype O97), Isolated from Carassius carassius with Motile Aeromonad Septicemia in China.Genome Announc. 2017 Jun 15;5(24):e00497-17. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00497-17. Genome Announc. 2017. PMID: 28619791 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carnahan AM, Joseph SW. Family I. Aeromonadaceae . In: Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT, editors. Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology. Vol. 2. New York, NY, USA: Springer; 2005.
-
- Noterdaeme L, Bigawa S, Willams KA, Ollevier F. Biochemical and physiological characteristics and plasmid profiles of Aeromonas hydrophila strains isolated from freshwater fish and from fresh water. Journal of Fish Diseases. 1991;14(3):313–321.
-
- Austin B, Austin DA. Bacterial Fish Pathogens. Disease of Farmed and Wild Fish. Chichester, UK: Praxis Publishing Ltd.; 2007.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

