Tomato juice intake suppressed serum concentration of 8-oxodG after extensive physical activity
- PMID: 22551119
- PMCID: PMC3494535
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2891-11-29
Tomato juice intake suppressed serum concentration of 8-oxodG after extensive physical activity
Abstract
Background: DNA is constantly exposed to reactive oxygen species (ROS), spontaneously arising during the normal oxygen metabolism. ROS may result in temporary as well as permanent modifications in various cellular components such as lipids, proteins and DNA, which may have deleterious consequences. Demonstrating that a dietary supplementation of antioxidants can reduce oxidative DNA damage may provide evidence for the value of such supplementation in prevention of cancer and age related diseases.
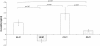
Findings: The present study was conducted to address whether tomato juice protects against ROS induced by extensive physical exercise in untrained individuals. As a marker of oxidative stress, serum levels of 8-oxodG were monitored using a modified ELISA. An intervention was performed involving 15 untrained healthy subjects who performed a 20 min physical exercise at 80% of maximum pulse using an ergometer bicycle. Blood samples were taken before and one hour after the exercise. The procedure was repeated after 5 weeks with a daily intake of 150 ml tomato juice and followed by a 5 weeks wash-out period and another 5 weeks with a daily intake of tomato juice. The results indicated that a daily intake of tomato juice, equal to 15 mg lycopene per day, for 5 weeks significantly reduced the serum levels of 8-oxodG after an extensive physical exercise.
Conclusion: These data strongly suggest that tomato juice has a potential antioxidant effect and may reduce the elevated level of ROS induced by oxidative stress.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Possible benefits of tomato juice consumption: a pilot study on irradiated human lymphocytes from healthy donors.Nutr J. 2017 May 12;16(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12937-017-0248-3. Nutr J. 2017. PMID: 28494764 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative DNA damage in prostate cancer patients consuming tomato sauce-based entrees as a whole-food intervention.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001 Dec 19;93(24):1872-9. doi: 10.1093/jnci/93.24.1872. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001. PMID: 11752012
-
Effect of consumption of tomato juice enriched with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on the lipid profile, antioxidant biomarker status, and cardiovascular disease risk in healthy women.Eur J Nutr. 2012 Jun;51(4):415-24. doi: 10.1007/s00394-011-0225-0. Epub 2011 Jul 14. Eur J Nutr. 2012. PMID: 21755327 Clinical Trial.
-
Tomato sauce supplementation and prostate cancer: lycopene accumulation and modulation of biomarkers of carcinogenesis.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2002 Nov;227(10):886-93. doi: 10.1177/153537020222701008. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2002. PMID: 12424330 Review.
-
Tomatoes versus lycopene in oxidative stress and carcinogenesis: conclusions from clinical trials.Eur J Clin Nutr. 2007 Mar;61(3):295-303. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602510. Epub 2006 Aug 16. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2007. PMID: 16929242 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA oxidation after exercise: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Physiol. 2023 Oct 31;14:1275867. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1275867. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 38028771 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of repeated bouts of long-duration endurance exercise on muscle and urinary levels of 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine in moderately trained cyclists.J Sports Sci. 2015;33(16):1692-701. doi: 10.1080/02640414.2015.1004637. Epub 2015 Jan 26. J Sports Sci. 2015. PMID: 25620316 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Damage Following Acute Aerobic Exercise: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Sports Med. 2020 Jan;50(1):103-127. doi: 10.1007/s40279-019-01181-y. Sports Med. 2020. PMID: 31529301 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Tomato Juice Intake on Salivary 8-Oxo-dG Levels as Oxidative Stress Biomarker after Extensive Physical Exercise.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Jan 14;2020:8948723. doi: 10.1155/2020/8948723. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32377311 Free PMC article.
-
Tomato juice intake increases resting energy expenditure and improves hypertriglyceridemia in middle-aged women: an open-label, single-arm study.Nutr J. 2015 Apr 8;14:34. doi: 10.1186/s12937-015-0021-4. Nutr J. 2015. PMID: 25880734 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

