Idiopathic premature ventricular contractions and ventricular tachycardias originating from the vicinity of tricuspid annulus: results of radiofrequency catheter ablation in thirty-five patients
- PMID: 22551200
- PMCID: PMC3393631
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2261-12-32
Idiopathic premature ventricular contractions and ventricular tachycardias originating from the vicinity of tricuspid annulus: results of radiofrequency catheter ablation in thirty-five patients
Abstract
Background: In recent years, catheter ablation has increasingly been used for ablation of idiopathic premature ventricular complexes (PVCs) or ventricular tachycardias (IVTs). However, the mapping and catheter ablation of the arrhythmias originating from the vicinity of tricuspid annulus (TA) may not be fully understood. This study aimed to investigate electrophysiologic characteristics and effects of radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFCA) for patients with symptomatic PVCs and IVTs originating from the vicinity of TA.
Methods: Characteristics of body surface electrocardiogram (ECG) and electrophysiologic recordings were analyzed in 35 patients with symptomatic PVCs/ IVTs originating from the vicinity of TA. RFCA was performed using pace mapping and activation mapping.
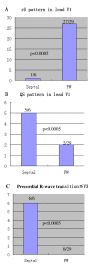
Results: Among the 35 patients with PVCs/IVTs arising from the vicinity of TA, complete elimination of PVCs/IVTs could be achieved by RFCA in 32 patients (success rate 91.43%) during a median follow-up period of 21 months. PVCs/IVTs originating from the vicinity of TA had distinctive ECG characteristics that were useful for identifying the precise origin. An rS pattern was recorded in lead V1 in 93.1% of patients with PVCs/IVTs from the free wall of TA, vs 16.7% of patients with PVCs/IVTs from the septal TA, whereas a QS pattern in lead V1 occurred in 83.3% of patients with PVCs/IVTs from the septal TA vs 6.9% of patients with PVCs from the free wall of the TA. The precordial R wave transition occurred by lead V3 or earlier in all patients with PVCs/IVTs originating from the septal portion of the TA, as compared to transition beyond V3 in all patients with PVCs/IVTs from the free wall of the TA.
Conclusions: RFCA is an effective curative therapy for symptomatic PVCs/IVTs originating from the vicinity of TA. There are specific characteristics in ECG and the ablation site could be located by ECG analysis.
Figures




References
-
- Wang K, Hodges M. The premature ventricular complex as a diagnostic aid. Ann Intern Med. 1992;117:766–770. - PubMed
-
- Li Jia, Li Yue-Chun, Ji Kang-Ting, Zhou Na-Dan, Lin Jia-Xuan, Zhang Wen-WU. et al.Premature ventricular contractions originating from the left ventricular septum: Results of Radiofrequency catheter ablation in twenty patients. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2011;11:27. doi: 10.1186/1471-2261-11-27. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

