Development of a low toxicity, effective pDNA vector based on noncovalent assembly of bioresponsive amino-β-cyclodextrin:adamantane-poly(vinyl alcohol)-poly(ethylene glycol) transfection complexes
- PMID: 22551467
- PMCID: PMC3417082
- DOI: 10.1021/bc2005158
Development of a low toxicity, effective pDNA vector based on noncovalent assembly of bioresponsive amino-β-cyclodextrin:adamantane-poly(vinyl alcohol)-poly(ethylene glycol) transfection complexes
Abstract
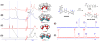
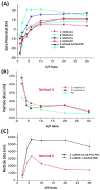
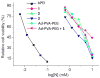
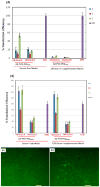
A host:guest-derived gene delivery vector has been developed, based on the self-assembly of cationic β-CD derivatives with a poly(vinyl alcohol) (MW 27 kDa) (PVA) main chain polymer bearing poly(ethylene glycol) (MW 750) (PEG) or MW 2000 PEG and acid-labile adamantane-modified (Ad) grafts through an acid-sensitive benzylidene acetal linkage. These components were investigated for their ability to promote supramolecular complex formation with pDNA using two different assembly schemes, involving either precomplexation of the pendent Ad-PVA-PEG polymer with the cationic β-CD derivatives before pDNA condensation (method A) or pDNA condensation with the cationic β-CD derivatives prior to addition of Ad-PVA-PEG to engage host:guest complexation (method B). The pendent polymers were observed to degrade under acidic conditions while remaining intact for more than 5 days at pH 7. HeLa cell culture data show that these materials have 10(3)-fold lower cytotoxicities than 25 kDa bPEI while maintaining transfection efficiencies that are superior to those observed for this benchmark cationic polymer transfection reagent when the method A assembly scheme is employed. These findings suggest that degradable cationic polymer constructs employing multivalent host:guest interactions may be an effective and low-toxicity vehicle for delivering nucleic acid cargo to target cells.
Figures
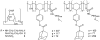

References
-
- Semple SC, Akinc A, Chen J, Sandhu AP, Mui BL, Cho CK, Sah DWY, Stebbing D, Crosley EJ, Yaworski E, Hafez IM, Dorkin JR, Qin J, Lam K, Rajeev KG, Wong KF, Jeffs LB, Nechev L, Eisenhardt ML, Jayaraman M, Kazem M, Maier MA, Srinivasulu M, Weinstein MJ, Chen Q, Alvarez R, Barros SA, De S, Klimuk SK, Borland T, Kosovrasti V, Cantley WL, Tam YK, Manoharan M, Ciufolini MA, Tracy MA, de Fougerolles A, MacLachlan I, Cullis PR, Madden TD, Hope MJ. Rational design of cationic lipids for siRNA delivery. Nature Biotech. 2010;20:172–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

