Macrophage p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activity regulates invariant natural killer T-cell responses during Borrelia burgdorferi infection
- PMID: 22551807
- PMCID: PMC3490691
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jis332
Macrophage p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activity regulates invariant natural killer T-cell responses during Borrelia burgdorferi infection
Abstract
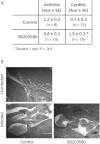
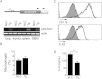
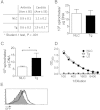
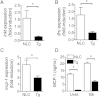
The interaction of macrophages with infectious agents leads to the activation of several signaling cascades, including mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases, such as p38. We now demonstrate that p38 MAP kinase-mediated responses are critical components to the immune response to Borrelia burgdorferi. The pharmacological and genetic inhibition of p38 MAP kinase activity during infection with the spirochete results in increased carditis. In transgenic mice that express a dominant negative form of p38 MAP kinase specifically in macrophages, production of the invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cell-attracting chemokine MCP-1 and of the antigen-presenting molecule CD1d are significantly reduced. The expression of the transgene therefore results in the deficient infiltration of iNKT cells, their decreased activation, and a diminished production of interferon γ (IFN-γ), leading to increased bacterial burdens and inflammation. These results show that p38 MAP kinase provides critical checkpoints for the protective immune response to the spirochete during infection of the heart.
Figures
References
-
- Wooten RM, Ma Y, Yoder RA, et al. Toll-like receptor 2 is required for innate, but not acquired, host defense to Borrelia burgdorferi. J Immunol. 2002;168:348–55. - PubMed
-
- Behera AK, Hildebrand E, Uematsu S, Akira S, Coburn J, Hu LT. Identification of a TLR-independent pathway for Borrelia burgdorferi-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinases and inflammatory mediators through binding to integrin α3β1. J Immunol. 2006;177:657–64. - PubMed
-
- Hirschfeld M, Kirschning CJ, Schwandner R, et al. Cutting edge: inflammatory signaling by Borrelia burgdorferi lipoproteins is mediated by toll-like receptor 2. J Immunol. 1999;163:2382–6. - PubMed
-
- Ebnet K, Brown KD, Siebenlist UK, Simon MM, Shaw S. Borrelia burgdorferi activates nuclear factor-kappa B and is a potent inducer of chemokine and adhesion molecule gene expression in endothelial cells and fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1997;158:3285–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

