The effect of combined calcium and cholecalciferol supplementation on bone mineral density in elderly women with moderate chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 22551881
- PMCID: PMC4030712
- DOI: 10.5414/cn107180
The effect of combined calcium and cholecalciferol supplementation on bone mineral density in elderly women with moderate chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Aims: To examine the effect of combined calcium and vitamin D3 supplementation on bone mineral density (BMD) inpatients with chronic kidney disease (CKD).
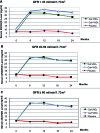
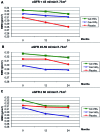
Methods: We performed a post-hoc analysis of the DECALYOS II, a 2-year randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 610 women randomized to: calcium-vitamin D3 fixed combination, calcium plus vitamin D3 separate combination, or placebo. Both active treatment groups received the same daily amount of calcium (1,200 mg) and vitamin D3 (800 IU). BMD of the distal radius was measured by single X-ray absorptiometry at baseline, 12 and 24 months.
Results: At baseline 47.2%, 36.4% and 16.4% of the study population had an eGFR ≥ 60, 45 -59, and < 45 ml/min/1.73 m2, respectively. Both active regimens vs. placebo markedly increased serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels from baseline in all eGFR groups (p 0.22 for all time points).
Conclusion: Combined calcium and vitamin D3 supplementation was effective in reducing rate of BMD loss in women with moderate CKD.
Figures
References
-
- Coresh J Selvin E Stevens LA Manzi J Kusek JW Eggers P Van Lente F Levey AS Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA. 2007; 298: 2038–2047. - PubMed
-
- Menon V Sarnak MJ The epidemiology of chronic kidney disease stages 1 to 4 and cardiovascular disease: a high-risk combination. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005; 45: 223–232. - PubMed
-
- Kendrick J Chonchol MB Nontraditional risk factors for cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic kidney disease. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2008; 4: 672–681. - PubMed
-
- Chonchol M Scragg R 25-Hydroxyvitamin D, insulin resistance, and kidney function in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Kidney Int. 2007; 71: 134–139. - PubMed
-
- Levin A Bakris GL Molitch M Smulders M Tian J Williams LA Andress DL Prevalence of abnormal serum vitamin D, PTH, calcium, and phosphorus in patients with chronic kidney disease: results of the study to evaluate early kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2007; 71: 31–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

