Variant brain-derived neurotrophic factor (Valine66Methionine) polymorphism contributes to developmental and estrous stage-specific expression of anxiety-like behavior in female mice
- PMID: 22552045
- PMCID: PMC3414635
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.03.032
Variant brain-derived neurotrophic factor (Valine66Methionine) polymorphism contributes to developmental and estrous stage-specific expression of anxiety-like behavior in female mice
Abstract
Background: Most anxiety and depressive disorders are twice as common in women compared with men, and the sex difference in prevalence typically emerges during adolescence. Hormonal changes across the menstrual cycle and during the postpartum and perimenopausal periods are associated with increased risk for anxiety and depression symptoms. In humans and animals, reduced brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) has been associated with increased expression of affective pathology. Recently, a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the BDNF gene (BDNF Valine66Methionine [Val66Met]), which reduces BDNF bioavailability, has been identified in humans and associated with a variety of neuropsychiatric disorders. Although BDNF expression can be directly influenced by estrogen and progesterone, the potential impact of the BDNF Val66Met SNP on sensitivity to reproductive hormone changes remains an open question.
Methods: As a predictive model, we used female mice in which the human SNP (BDNF Val66Met) was inserted into the mouse BDNF gene. Using standard behavioral paradigms, we tested the impact of this SNP on age and estrous-cycle-specific expression of anxiety-like behaviors.
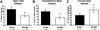
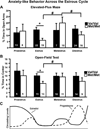
Results: Mice homozygous for the BDNF Val66Met SNP begin to exhibit increased anxiety-like behaviors over prepubertal and early adult development, show significant fluctuations in anxiety-like behaviors over the estrous cycle, and, as adults, differ from wild-type mice by showing significant fluctuations in anxiety-like behaviors over the estrous cycle-specifically, more anxiety-like behaviors during the estrus phase.
Conclusions: These findings have implications regarding the potential role of this SNP in contributing to developmental and reproductive hormone-dependent changes in affective disorders in humans.
Copyright © 2012 Society of Biological Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
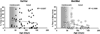
Comment in
-
BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels across the female life span: implications for the sex bias in affective disorders.Biol Psychiatry. 2012 Sep 15;72(6):434-6. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.07.018. Biol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22906753 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Weissman MM, Bland RC, Canino GJ, Faravelli C, Greenwald S, Hwu HG, et al. Cross-national epidemiology of major depression and bipolar disorder. JAMA. 1996;276(4):293–299. - PubMed
-
- Gater R, Tansella M, Korten A, Tiemens BG, Mavreas VG, Olatawura MO. Sex differences in the prevalence and detection of depressive and anxiety disorders in general health care settings: report from the World Health Organization Collaborative Study on Psychological Problems in General Health Care. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998;55(5):405–413. - PubMed
-
- Kessler RC, McGonagle KA, Swartz M, Blazer DG, Nelson CB. Sex and depression in the National Comorbidity Survey. I: Lifetime prevalence, chronicity and recurrence. J Affect Disord. 1993;29(2–3):85–96. - PubMed
-
- Bromberger JT, Assmann SF, Avis NE, Schocken M, Kravitz HM, Cordal A. Persistent mood symptoms in a multiethnic community cohort of pre- and perimenopausal women. Am J Epidemiol. 2003;158(4):347–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RC1 MH088814/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS007080/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MH082528/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS052819/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MH060478/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F30 MH082528/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- NS052819/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007739/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R25 MH060478/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH088814/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- NS07080/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- GM07739/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH079513/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

