Oncogenic PI3K mutations lead to NF-κB-dependent cytokine expression following growth factor deprivation
- PMID: 22552288
- PMCID: PMC3541677
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-4141
Oncogenic PI3K mutations lead to NF-κB-dependent cytokine expression following growth factor deprivation
Abstract
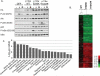
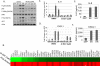
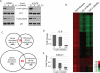
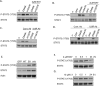
The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway is one of the most commonly misregulated signaling pathways in human cancers, but its impact on the tumor microenvironment has not been considered as deeply as its autonomous impact on tumor cells. In this study, we show that NF-κB is activated by the two most common PI3K mutations, PIK3CA E545K and H1047R. We found that markers of NF-κB are most strongly upregulated under conditions of growth factor deprivation. Gene expression analysis conducted on cells deprived of growth factors identified the repertoire of genes altered by oncogenic PI3K mutations following growth factor deprivation. This gene set most closely correlated with gene signatures from claudin-low and basal-like breast tumors, subtypes frequently exhibiting constitutive PI3K/Akt activity. An NF-κB-dependent subset of genes driven by oncogenic PI3K mutations was also identified that encoded primarily secreted proteins, suggesting a paracrine role for this gene set. Interestingly, while NF-κB activated by oncogenes such as Ras and EGF receptor leads to cell-autonomous effects, abrogating NF-κB in PI3K-transformed cells did not decrease proliferation or induce apoptosis. However, conditioned media from PI3K mutant-expressing cells led to increased STAT3 activation in recipient THP-1 monocytes or normal epithelial cells in a NF-κB and interleukin-6-dependent manner. Together, our findings describe a PI3K-driven, NF-κB-dependent transcriptional profile that may play a critical role in promoting a microenvironment amenable to tumor progression. These data also indicate that NF-κB plays diverse roles downstream from different oncogenic signaling pathways.
©2012 AACR.
Figures


References
-
- Cantley LC. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science. 2002;296(5573):1655–7. - PubMed
-
- Luo J, Manning BD, Cantley LC. Targeting the PI3K-Akt pathway in human cancer: rationale and promise. Cancer cell. 2003;4(4):257–62. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Luo J, Cantley LC. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7(8):606–19. - PubMed
-
- Vivanco I, Sawyers CL. The phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nature reviews Cancer. 2002;2(7):489–501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 AI035098/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA075080/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA138255/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA148761/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA75080/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA138255/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA138937/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA148761/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI035098/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA73756/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA073756/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI35098/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA058223/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50-CA58223/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

