Combined EGFR/MET or EGFR/HSP90 inhibition is effective in the treatment of lung cancers codriven by mutant EGFR containing T790M and MET
- PMID: 22552292
- PMCID: PMC3389159
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3720
Combined EGFR/MET or EGFR/HSP90 inhibition is effective in the treatment of lung cancers codriven by mutant EGFR containing T790M and MET
Abstract
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) that target the EGF receptor (EGFR) are effective in most non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) patients whose tumors harbor activating EGFR kinase domain mutations. Unfortunately, acquired resistance eventually emerges in these chronically treated cancers. Two of the most common mechanisms of acquired resistance to TKIs seen clinically are the acquisition of a secondary "gatekeeper" T790M EGFR mutation that increases the affinity of mutant EGFR for ATP and activation of MET to offset the loss of EGFR signaling. Although up to one-third of patient tumors resistant to reversible EGFR TKIs harbor concurrent T790M mutation and MET amplification, potential therapies for these tumors have not been modeled in vivo. In this study, we developed a preclinical platform to evaluate potential therapies by generating transgenic mouse lung cancer models expressing EGFR-mutant Del19-T790M or L858R-T790M, each with concurrent MET overexpression. We found that monotherapy targeting EGFR or MET alone did not produce significant tumor regression. In contrast, combination therapies targeting EGFR and MET simultaneously were highly efficacious against EGFR TKI-resistant tumors codriven by Del19-T790M or L858R-T790M and MET. Our findings therefore provide an in vivo model of intrinsic resistance to reversible TKIs and offer preclinical proof-of-principle that combination targeting of EGFR and MET may benefit patients with NSCLC.
©2012 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
On behalf of all authors on this manuscript, following conflicts of interest that need to be disclosed. All authors have completed separate conflict of interest forms and we have no other conflicts of interest to report.
Drs. Jänne and Engelman have following ownership and consulting relationship.
(Minor $10,000 or less)
Astra Zeneca, Boehringher Ingelheim, Pfizer, Roche, Genentech.
(Major $10,000 or more)
Lab Corp
(Minor $10,000 or less)
Ventanan/Roche
(Minor $10,000 or less)
Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech, Glaxo Smith Kline, Roche, Sanofi Aventis
Figures
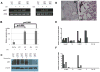
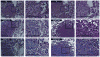
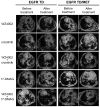

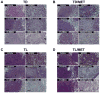
References
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–39. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–500. - PubMed
-
- Sordella R, Bell DW, Haber DA, Settleman J. Gefitinib-sensitizing EGFR mutations in lung cancer activate anti-apoptotic pathways. Science. 2004;305:1163–7. - PubMed
-
- Chen HJ, Mok TS, Chen ZH, Guo AL, Zhang XC, Su J, et al. Clinicopathologic and molecular features of epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutation and c-MET amplification in tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant Chinese non-small cell lung cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 2009;15:651–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

