Nicotine exposure and the progression of chronic kidney disease: role of the α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
- PMID: 22552933
- PMCID: PMC3404588
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00661.2011
Nicotine exposure and the progression of chronic kidney disease: role of the α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Abstract
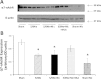
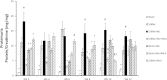
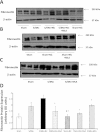
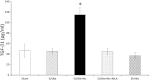
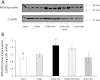
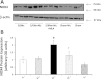
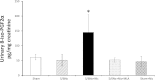
Clinical studies have established the role of cigarette smoking as a risk factor in the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD). We have shown that nicotine promotes mesangial cell proliferation and hypertrophy via nonneuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). The α7-nAChR is one of the most important subunits of the nAChRs. These studies were designed to test the hypothesis that nicotine worsens renal injury in rats with 5/6 nephrectomy (5/6Nx) and that the α7-nAChR subunit is required for these effects. We studied five different groups: Sham, 5/6Nx, 5/6Nx + nicotine (Nic; 100 μg/ml dry wt), 5/6Nx + Nic + α7-nAChR blocker methyllicaconitine (MLA; 3 mg·kg(-1)·day(-1) sq), and Sham + Nic. Blood pressure was measured by the tail-cuff method, and urine was collected for proteinuria. After 12 wk, the rats were euthanized and kidneys were collected. We observed expression of the α7-nAChR in the proximal and distal tubules. The administration of nicotine induced a small increase in blood pressure and resulted in cotinine levels similar to those found in the plasma of smokers. In 5/6Nx rats, the administration of nicotine significantly increased urinary protein excretion (onefold), worsened the glomerular injury score and increased fibronectin (∼ 50%), NADPH oxidase 4 (NOX4; ∼100%), and transforming growth factor-β expression (∼200%). The administration of nicotine to sham rats increased total proteinuria but not albuminuria, suggesting direct effects on tubular protein reabsorption. These effects were prevented by MLA, demonstrating a critical role for the α7-nAChR as a mediator of the effects of nicotine in the progression of CKD.
Figures



References
-
- Bedard K, Krause KH. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 87: 245–313, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Bleyer AJ, Shemanski LR, Burke GL, Hansen KJ, Appel RG. Tobacco, hypertension, and vascular disease: risk factors for renal functional decline in an older population. Kidney Int 57: 2072–2079, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Boyle P. Cancer, cigarette smoking and premature death in Europe: a review including the Recommendations of European Cancer Experts Consensus Meeting, Helsinki, October 1996. Lung Cancer 17: 1–60, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Cachat F, Meagher-Villemure K, Guignard JP. Lymphomatoid granulomatosis in a renal transplant patient. Pediatr Nephrol 18: 838–842, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Carmona R. The Health Consequences of Involuntary Exposure to Tobacco Smoke: A Report of the Surgeon General. Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 2006, p. iii - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

