Dilemmas concerning dose distribution and the influence of relative biological effect in proton beam therapy of medulloblastoma
- PMID: 22553304
- PMCID: PMC3474038
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr/24498486
Dilemmas concerning dose distribution and the influence of relative biological effect in proton beam therapy of medulloblastoma
Abstract
Objective: To improve medulloblastoma proton therapy. Although considered ideal for proton therapy, there are potential disadvantages. Expected benefits include reduced radiation-induced cancer and circulatory complications, while avoiding small brain volumes of dose in-homogeneity when compared with conventional X-rays. Several aspects of proton therapy might contribute to reduced tumour control due to (a) the use of more homogenous dose levels which can result in under-dosage, (b) differences in relative biological effectiveness (RBE) between that prescription RBE of 1.1 and the RBE of brain and spinal cord (likely to exceed 1.1) and in medulloblastoma cells (where RBE is likely to be below 1.1). Such changes, although speculative for RBE, might result in potential underdosage of tumour cells and a higher bio-effect in brain tissue.
Methods: Dose distributions for X-ray and proton treatment are compared, with allocation of likely RBE values for fast growing medullolastoma cells and stable central nervous system tissue.
Results: These physical and radiobiological factors are shown to combine to give a higher risk of tumour recurrence with further risks on tumour control when dose reduction schedules used for X-ray therapy are replicated for proton therapy for "low-risk" patients.
Conclusion: The dose distributions and prescribed doses of proton therapy, taking into account RBE, in children and adults with medulloblastoma, need to be reconsidered.
Figures

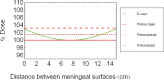

References
-
- Yock T, DeLaney TF, Esty B, Tarbell NJ. Pediatric tumours. Proton and charged particle radiotherapy. Delaney TF, Kooy HM, eds. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins; 2008. pp. 125–30
-
- Lee CT, Bilton SD, Famiglietti RM, Riley BA, Mahajan A, Chang EL, et al. Treatment planning with protons for pediatric retinoblastoma, medulloblastoma, and pelvic sarcoma: how do protons compare with other conformal techniques? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2005;63:362–72 - PubMed
-
- St Clair WH, Adams JA, Bues M, Fullerton BC, La Shell S, Kooy HM, et al. Advantage of protons compared to conventional X-ray or IMRT in the treatment of a pediatric patient with medulloblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2004;58:727–34 - PubMed
-
- Cochran DM, Yock TI, Adams JA, Tarbell NJ. Radiation dose to the lens during craniospinal irradiation—an improvement in proton radiotherapy technique. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2008;70:1336–42 - PubMed
-
- Miralbell R, Lomax A, Cella L, Schneider U. Potential reduction of the incidence of radiation-induced second cancers by using proton beams in the treatment of pediatric tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2002;54:824–9 - PubMed

