EVI1 is critical for the pathogenesis of a subset of MLL-AF9-rearranged AMLs
- PMID: 22553314
- PMCID: PMC3382941
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-11-393827
EVI1 is critical for the pathogenesis of a subset of MLL-AF9-rearranged AMLs
Abstract
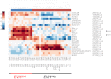
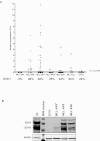
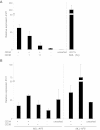
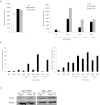
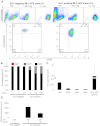
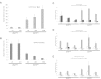
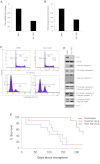
The proto-oncogene EVI1 (ecotropic viral integration site-1), located on chromosome band 3q26, is aberrantly expressed in human acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with 3q26 rearrangements. In the current study, we showed, in a large AML cohort carrying 11q23 translocations, that ∼ 43% of all mixed lineage leukemia (MLL)-rearranged leukemias are EVI1(pos). High EVI1 expression occurs in AMLs expressing the MLL-AF6, -AF9, -AF10, -ENL, or -ELL fusion genes. In addition, we present evidence that EVI1(pos) MLL-rearranged AMLs differ molecularly, morphologically, and immunophenotypically from EVI1(neg) MLL-rearranged leukemias. In mouse bone marrow cells transduced with MLL-AF9, we show that MLL-AF9 fusion protein maintains Evi1 expression on transformation of Evi1(pos) HSCs. MLL-AF9 does not activate Evi1 expression in MLL-AF9-transformed granulocyte macrophage progenitors (GMPs) that were initially Evi1(neg). Moreover, shRNA-mediated knockdown of Evi1 in an Evi1(pos) MLL-AF9 mouse model inhibits leukemia growth both in vitro and in vivo, suggesting that Evi1 provides a growth-promoting signal. Using the Evi1(pos) MLL-AF9 mouse leukemia model, we demonstrate increased sensitivity to chemotherapeutic agents on reduction of Evi1 expression. We conclude that EVI1 is a critical player in tumor growth in a subset of MLL-rearranged AMLs.
Figures
References
-
- Bullinger L, Döhner K, Bair E, et al. Use of gene-expression profiling to identify subclasses in adult acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(16):1605–1616. - PubMed
-
- Valk PJ, Verhaak RG, Beijen MA, et al. Prognostically useful gene-expression profiles in acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(16):1617–1628. - PubMed
-
- Morishita K, Parker DS, Mucenski ML, et al. Retroviral activation of a novel gene encoding a zinc finger protein in IL-3-dependent myeloid leukemia cell lines. Cell. 1988;54(6):831–840. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

