Activation of cap-dependent translation by mucosal human papillomavirus E6 proteins is dependent on the integrity of the LXXLL binding motif
- PMID: 22553330
- PMCID: PMC3416298
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00487-12
Activation of cap-dependent translation by mucosal human papillomavirus E6 proteins is dependent on the integrity of the LXXLL binding motif
Abstract
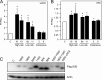
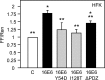
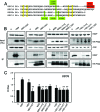
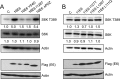
The human papillomavirus (HPV) type 16 (HPV16) E6 protein can stimulate mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling and cap-dependent translation through activation of the PDK1 and mTORC2 kinases. Here we report that HPV18 E6 also enhances cap-dependent translation. The integrity of LXXLL and PDZ protein binding domains is important for activation of cap-dependent translation by high-risk mucosal HPV E6 proteins. Consistent with this model, low-risk mucosal HPV6b and HPV11 E6 proteins, which do not contain a PDZ protein binding motif, also activate cap-dependent translation and mTORC1, albeit at a lower efficiency than high-risk HPV E6 proteins. In contrast, cutaneous HPV5 and HPV8 E6 proteins, which lack LXXLL and PDZ motif protein binding, do not enhance cap-dependent translation. Mutagenic analyses of low-risk HPV E6 proteins revealed that association with the LXXLL motif containing ubiquitin ligase E6AP (UBE3A) correlates with activation of cap-dependent translation. Hence, activation of mTORC1 and cap-dependent translation may be important for the viral life cycle in specific epithelial tissue types and contribute to cellular transformation in cooperation with other biological activities of high-risk HPV E6-containing proteins.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The human papillomavirus type 16 E6 oncoprotein activates mTORC1 signaling and increases protein synthesis.J Virol. 2010 Sep;84(18):9398-407. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00974-10. Epub 2010 Jul 14. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20631133 Free PMC article.
-
High-Risk Mucosal Human Papillomavirus 16 (HPV16) E6 Protein and Cutaneous HPV5 and HPV8 E6 Proteins Employ Distinct Strategies To Interfere with Interferon Regulatory Factor 3-Mediated Beta Interferon Expression.J Virol. 2022 May 25;96(10):e0187521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01875-21. Epub 2022 Apr 27. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35475668 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Two Oncogenic Functional Sites of the HPV E6 Oncoprotein with a High-Affinity Bivalent Ligand.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015 Jun 26;54(27):7958-62. doi: 10.1002/anie.201502646. Epub 2015 May 27. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015. PMID: 26014966 Free PMC article.
-
E6 and E7 from human papillomavirus type 16 cooperate to target the PDZ protein Na/H exchange regulatory factor 1.J Virol. 2011 Aug;85(16):8208-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00114-11. Epub 2011 Jun 15. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21680517 Free PMC article.
-
The biology of papillomavirus PDZ associations: what do they offer papillomaviruses?Curr Opin Virol. 2021 Dec;51:119-126. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2021.09.011. Epub 2021 Oct 13. Curr Opin Virol. 2021. PMID: 34655911 Review.
Cited by
-
The Human Papillomavirus 16 E7 Oncoprotein Attenuates AKT Signaling To Promote Internal Ribosome Entry Site-Dependent Translation and Expression of c-MYC.J Virol. 2016 May 27;90(12):5611-5621. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00411-16. Print 2016 Jun 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27030265 Free PMC article.
-
Papillomavirus E6 oncoproteins.Virology. 2013 Oct;445(1-2):115-37. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.04.026. Epub 2013 May 24. Virology. 2013. PMID: 23711382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Functional Motifs Utilized by Viruses.Proteomes. 2016 Jan 21;4(1):3. doi: 10.3390/proteomes4010003. Proteomes. 2016. PMID: 28248213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phase I study of induction chemotherapy with afatinib, ribavirin, and weekly carboplatin and paclitaxel for stage IVA/IVB human papillomavirus-associated oropharyngeal squamous cell cancer.Head Neck. 2018 Feb;40(2):233-241. doi: 10.1002/hed.24938. Epub 2017 Sep 30. Head Neck. 2018. PMID: 28963790 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Proteomic analysis and identification of cellular interactors of the giant ubiquitin ligase HERC2.J Proteome Res. 2015 Feb 6;14(2):953-66. doi: 10.1021/pr501005v. Epub 2014 Dec 15. J Proteome Res. 2015. PMID: 25476789 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen JJ, Reid CE, Band V, Androphy EJ. 1995. Interaction of papillomavirus E6 oncoproteins with a putative calcium-binding protein. Science 269:529–531 - PubMed
-
- Elston RC, Napthine S, Doorbar J. 1998. The identification of a conserved binding motif within human papillomavirus type 16 E6 binding peptides, E6AP and E6BP. J. Gen. Virol. 79(Pt 2):371–374 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

