Local control of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate signaling in the Golgi apparatus by Vps74 and Sac1 phosphoinositide phosphatase
- PMID: 22553352
- PMCID: PMC3386216
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E12-01-0077
Local control of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate signaling in the Golgi apparatus by Vps74 and Sac1 phosphoinositide phosphatase
Abstract
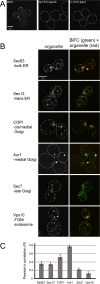
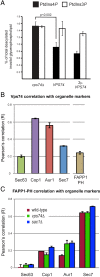
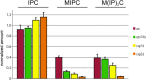
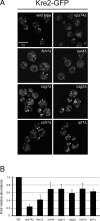
In the Golgi apparatus, lipid homeostasis pathways are coordinated with the biogenesis of cargo transport vesicles by phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases (PI4Ks) that produce phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PtdIns4P), a signaling molecule that is recognized by downstream effector proteins. Quantitative analysis of the intra-Golgi distribution of a PtdIns4P reporter protein confirms that PtdIns4P is enriched on the trans-Golgi cisterna, but surprisingly, Vps74 (the orthologue of human GOLPH3), a PI4K effector required to maintain residence of a subset of Golgi proteins, is distributed with the opposite polarity, being most abundant on cis and medial cisternae. Vps74 binds directly to the catalytic domain of Sac1 (K(D) = 3.8 μM), the major PtdIns4P phosphatase in the cell, and PtdIns4P is elevated on medial Golgi cisternae in cells lacking Vps74 or Sac1, suggesting that Vps74 is a sensor of PtdIns4P level on medial Golgi cisternae that directs Sac1-mediated dephosphosphorylation of this pool of PtdIns4P. Consistent with the established role of Sac1 in the regulation of sphingolipid biosynthesis, complex sphingolipid homeostasis is perturbed in vps74Δ cells. Mutant cells lacking complex sphingolipid biosynthetic enzymes fail to properly maintain residence of a medial Golgi enzyme, and cells lacking Vps74 depend critically on complex sphingolipid biosynthesis for growth. The results establish additive roles of Vps74-mediated and sphingolipid-dependent sorting of Golgi residents.
Figures
References
-
- Bretscher MS, Munro S. Cholesterol and the Golgi apparatus. Science. 1993;261:1280–1281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

