Betulinic acid targets YY1 and ErbB2 through cannabinoid receptor-dependent disruption of microRNA-27a:ZBTB10 in breast cancer
- PMID: 22553354
- PMCID: PMC4924623
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0026
Betulinic acid targets YY1 and ErbB2 through cannabinoid receptor-dependent disruption of microRNA-27a:ZBTB10 in breast cancer
Abstract
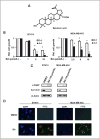
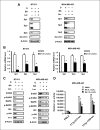
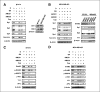
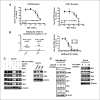
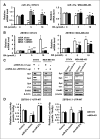
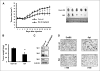
Treatment of ErbB2-overexpressing BT474 and MDA-MB-453 breast cancer cells with 1 to 10 μmol/L betulinic acid inhibited cell growth, induced apoptosis, downregulated specificity protein (Sp) transcription factors Sp1, Sp3, and Sp4, and decreased expression of ErbB2. Individual or combined knockdown of Sp1, Sp3, Sp4 by RNA interference also decreased expression of ErbB2 and this response was because of repression of YY1, an Sp-regulated gene. Betulinic acid-dependent repression of Sp1, Sp3, Sp4, and Sp-regulated genes was due, in part, to induction of the Sp repressor ZBTB10 and downregulation of microRNA-27a (miR-27a), which constitutively inhibits ZBTB10 expression, and we show for the first time that the effects of betulinic acid on the miR-27a:ZBTB10-Sp transcription factor axis were cannabinoid 1 (CB1) and CB2 receptor-dependent, thus identifying a new cellular target for this anticancer agent.
©2012 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Alakurtti S, Makela T, Koskimies S, Yli-Kauhaluoma J. Pharmacological properties of the ubiquitous natural product betulin. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2006;29:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Pisha E, Chai H, Lee IS, Chagwedera TE, Farnsworth NR, Cordell GA, et al. Discovery of betulinic acid as a selective inhibitor of human melanoma that functions by induction of apoptosis. Nat Med. 1995;1:1046–51. - PubMed
-
- Fulda S, Kroemer G. Targeting mitochondrial apoptosis by betulinic acid in human cancers. Drug Discov Today. 2009;14:885–90. - PubMed
-
- Fulda S, Scaffidi C, Susin SA, Krammer PH, Kroemer G, Peter ME, et al. Activation of mitochondria and release of mitochondrial apoptogenic factors by betulinic acid. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:33942–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

