The histone H3 lysine 56 acetylation pathway is regulated by target of rapamycin (TOR) signaling and functions directly in ribosomal RNA biogenesis
- PMID: 22553361
- PMCID: PMC3413144
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks345
The histone H3 lysine 56 acetylation pathway is regulated by target of rapamycin (TOR) signaling and functions directly in ribosomal RNA biogenesis
Abstract
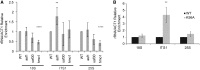
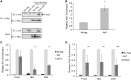
Epigenetic changes in chromatin through histone post-translational modifications are essential for altering gene transcription in response to environmental cues. How histone modifications are regulated by environmental stimuli remains poorly understood yet this process is critical for delineating how epigenetic pathways are influenced by the cellular environment. We have used the target of rapamycin (TOR) pathway, which transmits environmental nutrient signals to control cell growth, as a model to delineate mechanisms underlying this phenomenon. A chemical genomics screen using the TOR inhibitor rapamycin against a histone H3/H4 mutant library identified histone H3 lysine 56 acetylation (H3K56ac) as a chromatin modification regulated by TOR signaling. We demonstrate this acetylation pathway functions in TOR-dependent cell growth in part by contributing directly to ribosomal RNA (rRNA) biogenesis. Specifically, H3K56ac creates a chromatin environment permissive to RNA polymerase I transcription and nascent rRNA processing by regulating binding of the high mobility group protein Hmo1 and the small ribosomal subunit (SSU) processome complex. Overall, these studies identify a novel chromatin regulatory role for TOR signaling and support a specific function for H3K56ac in ribosomal DNA (rDNA) gene transcription and nascent rRNA processing essential for cell growth.
Figures
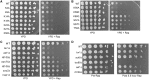
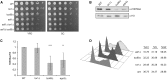
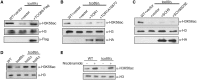
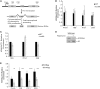
References
-
- Dazert E, Hall MN. mTOR signaling in disease. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 23:744–755. - PubMed
-
- Heitman J, Movva NR, Hall MN. Targets for cell cycle arrest by the immunosuppressant rapamycin in yeast. Science. 1991;253:905–909. - PubMed
-
- Brown EJ, Albers MW, Shin TB, Ichikawa K, Keith CT, Lane WS, Schreiber SL. A mammalian protein targeted by G1-arresting rapamycin-receptor complex. Nature. 1994;369:756–758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

