Hyperglycemia and a common variant of GCKR are associated with the levels of eight amino acids in 9,369 Finnish men
- PMID: 22553379
- PMCID: PMC3379649
- DOI: 10.2337/db11-1378
Hyperglycemia and a common variant of GCKR are associated with the levels of eight amino acids in 9,369 Finnish men
Abstract
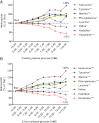
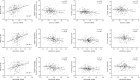
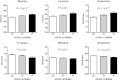
We investigated the association of glycemia and 43 genetic risk variants for hyperglycemia/type 2 diabetes with amino acid levels in the population-based Metabolic Syndrome in Men (METSIM) Study, including 9,369 nondiabetic or newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic Finnish men. Plasma levels of eight amino acids were measured with proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Increasing fasting and 2-h plasma glucose levels were associated with increasing levels of several amino acids and decreasing levels of histidine and glutamine. Alanine, leucine, isoleucine, tyrosine, and glutamine predicted incident type 2 diabetes in a 4.7-year follow-up of the METSIM Study, and their effects were largely mediated by insulin resistance (except for glutamine). We also found significant correlations between insulin sensitivity (Matsuda insulin sensitivity index) and mRNA expression of genes regulating amino acid degradation in 200 subcutaneous adipose tissue samples. Only 1 of 43 risk single nucleotide polymorphisms for type 2 diabetes or hyperglycemia, the glucose-increasing major C allele of rs780094 of GCKR, was significantly associated with decreased levels of alanine and isoleucine and elevated levels of glutamine. In conclusion, the levels of branched-chain, aromatic amino acids and alanine increased and the levels of glutamine and histidine decreased with increasing glycemia, reflecting, at least in part, insulin resistance. Only one single nucleotide polymorphism regulating hyperglycemia was significantly associated with amino acid levels.
Figures
References
-
- Felig P. Amino acid metabolism in man. Annu Rev Biochem 1975;44:933–955 - PubMed
-
- Jefferson LS, Li JB, Rannels SR. Regulation by insulin of amino acid release and protein turnover in the perfused rat hemicorpus. J Biol Chem 1977;252:1476–1483 - PubMed
-
- Biolo G, Williams BD, Fleming RY, Wolfe RR. Insulin action on muscle protein kinetics and amino acid transport during recovery after resistance exercise. Diabetes 1999;48:949–957 - PubMed
-
- van Loon LJ, Kruijshoop M, Menheere PP, Wagenmakers AJ, Saris WH, Keizer HA. Amino acid ingestion strongly enhances insulin secretion in patients with long-term type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003;26:625–630 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

