Effects of flavone on the oxidation-induced injury of retinal pigment epithelium cells
- PMID: 22553529
- PMCID: PMC3340770
- DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2010.02.02
Effects of flavone on the oxidation-induced injury of retinal pigment epithelium cells
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effect of flavone on oxidation-induced injury in retinal pigment epithelium cells.
Methods: In in vivo studies, NaIO(3)-induced RPE degeneration in rat eyes was treated with 0.5% flavone eye drops 3 times a day for 1 week before and 4 weeks after NaIO(3) injection. At the end of 2 and 4 weeks, all rats were measured c-wave by electroretinogram (ERG). In in vitro studies, ARPE-19 cells were treated with hypoxia, H(2)O(2), NaN(3) and t-BHP to induce cell damages. MTT assay was used to measure the viable cells.
Results: The ERG c-wave results showed that flavone reversed NaIO(3)-induced injury at the end of 4 weeks. In vitro results showed flavone reversed the various oxidants-induced injuries in RPE cells.
Conclusion: Flavone could prevent the RPE from oxidation-induced injury both in vivo and in vitro.
Keywords: age-related macular degeneration; flavone; oxidation; retinal pigment epithelium.
Figures





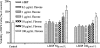
Similar articles
-
Effect of Tetramethylpyrazine on RPE degeneration, choroidal blood flow and oxidative stress of RPE cells.Int J Ophthalmol. 2010;3(3):205-10. doi: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2010.03.06. Epub 2010 Sep 18. Int J Ophthalmol. 2010. PMID: 22553555 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of naringenin on NaIO(3)-induced retinal pigment epithelium degeneration and laser-induced choroidal neovascularization in rats.Int J Ophthalmol. 2010;3(1):5-8. doi: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2010.01.02. Epub 2010 Mar 18. Int J Ophthalmol. 2010. PMID: 22553507 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of cytokeratin 17 on retinal pigment epithelium degeneration and choroidal neovascularization.Int J Ophthalmol. 2016 Mar 18;9(3):363-8. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2016.03.06. eCollection 2016. Int J Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 27158603 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Guanabenz on Rat AMD Models and Rabbit Choroidal Blood Flow.Open Ophthalmol J. 2011;5:27-31. doi: 10.2174/1874364101105010027. Epub 2011 Apr 28. Open Ophthalmol J. 2011. PMID: 21633720 Free PMC article.
-
[Retinal pigment epithelial cell transplantation: perspective].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 1996 Dec;100(12):982-1006. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 1996. PMID: 9022310 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
African and Asian Mitochondrial DNA Haplogroups Confer Resistance Against Diabetic Stresses on Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cybrid Cells In Vitro.Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Mar;57(3):1636-1655. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01834-z. Epub 2019 Dec 6. Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 31811564 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin inhibits NaIO3-induced ARPE-19 cell apoptosis via suppression of HIF-1α/BNIP3-LC3B/mitophagy signaling.Cell Biosci. 2022 Aug 19;12(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00879-3. Cell Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35986432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fine SL, Berger JW, Maguire MG, Ho AC. Age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:483–492. - PubMed
-
- Klein R, Peto T, Bird A, Vannewkirk MR. The epidemiology of age-related macular degeneration. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004;137:486–495. - PubMed
-
- Kuehn BM. Gene discovery provides clues to cause of age-related macular degeneration. JAMA. 2005;293:1841–1845. - PubMed
-
- Klein R. The five-year incidence and progression of age-related maculopathy: the Beaver Dam Eye Study. Ophthalmology. 1997;104:7–21. - PubMed
-
- Lin B, Chiou GCY. Antioxidant activity of naringenin on various oxidants induced damages in ARPE-19 cells and HUVEC. Int J Ophthalmol (Guoji Yanke Zazhi) 2008;8:1963–1967.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
