Effect of CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells in the development of anterior chamber-associated immune deviation
- PMID: 22553601
- PMCID: PMC3340679
- DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2011.01.04
Effect of CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells in the development of anterior chamber-associated immune deviation
Abstract
Aim: To investigate whether CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T (Treg) cells play a role in the development of anterior chamber-associated immune deviation (ACAID).
Methods: The dynamic changes in the frequency of CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells, CD4(+)CD25(+) FoxP3(+) T cells and CD4(+)CD25(+) PD-1(+) T cells from spleens of mice with ACAID were analyzed by flow cytometry. Foxp3 mRNA expression in purified CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells was analyzed using real-time PCR. The suppressive effect of purified CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells on the proliferation of CD4(+)CD25(-) T cells was evaluated by [(3)H] thymidine incorporation. A blocking experiment was performed to further address the role of CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells in ACAID. The expression of IL-10 in purified CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells was evaluated by ELISA.
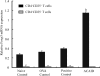
Results: Increased frequencies of CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells, CD4(+)CD25(+) FoxP3(+) T cells and CD4(+)CD25(+) PD-1(+) T cells were observed in ACAID. The CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells from mice with ACAID showed enhanced suppressive effect on the proliferation of CD4(+)CD25(-) T cells. Treatment of BALB/c mice with anti-CD25 antibody after injection of OVA into the anterior chamber significantly inhibited the induction of ACAID. Furthermore, purified CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells from ACAID mice secreted IL-10.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that Treg cells are induced in the mice undergoing ACAID. These Treg cells may play a role in the development of ACAID.
Keywords: ACAID; CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells; Foxp3; IL-10; PD-1.
Figures
References
-
- Schwartz RH. Natural regulatory T cells and self-tolerance. Nat Immunol. 2005;6(4):327–330. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising Foxp3-expressing CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells in immunological tolerance to self and non-self. Nat Immunol. 2005;6(4):345–352. - PubMed
-
- Hawrylowicz CM, O'Garra A. Potential role of interleukin-10-secreting regulatory T cells in allergy and asthma. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5(4):271–283. - PubMed
-
- Birebent B, Lorho R, Lechartier H, de Guibert S, Alizadeh M, Vu N, Beauplet A, Robillard N, Semana G. Suppressive properties of human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells are dependent on CTLA-4 expression. Eur J Immunol. 2004;34(12):3485–3496. - PubMed
-
- Tang Q, Boden EK, Henriksen KJ, Bour-Jordan H, Bi M, Bluestone JA. Distinct roles of CTLA-4 and TGF-beta in CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell function. Eur J Immunol. 2004;34(11):2996–3005. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials