Effect of Bak Foong Pills on the expression of β-amyloid in rat retina with optic nerve transection
- PMID: 22553610
- PMCID: PMC3340674
- DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2011.01.13
Effect of Bak Foong Pills on the expression of β-amyloid in rat retina with optic nerve transection
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effect of Bak Foong Pills (BFP) on the expression of β-amyloid (Aβ) in rats retina with optic nerve transection, and its roles and possible mechanisms in protecting optic nerve damage.
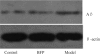
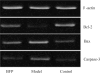
Methods: Seventy-two healthy, Sprague-Dawley, adult rats were randomly assigned to three groups: negative control group (control group), optic nerve transection group (model group) and BFP treatment group (BFP group, 100μg/mL) followed by establishing optic nerve transection model. The expression of Aβ was measured at 48 hours by Western-blotting. Moreover, the expressions of Bcl-2, Bax and Caspase-3 mRNA were evaluated at 48 hours by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
Results: There were significant differences among the control, model and BFP groups in the expression of Aβ (all P<0.01). Aβ expression was significantly higher in the model and BFP groups than that in the control group (P<0.01), with a more significant reduction in the BFP group than that in the model group (P<0.01). Moreover, there were also significant differences among the three groups in the expressions of Bcl-2/Bax (Bcl-2: anti-apoptotic; Bax: proapoptotic) and Caspase-3 mRNA (proapoptotic) (all P<0.01). Bcl-2/Bax ratio was significantly lower and Caspase-3 mRNA expression was significantly higher in the model and BFP groups than those in the control group (P<0.01), with a significant growing of Bcl-2/Bax and reduction of Caspase-3 in the BFP group than those in the model group (P<0.01).
Conclusion: BFP can down-regulate Aβ expression in retina and may inhibit apoptosis and protect optic nerve by enhancing Bcl-2/Bax ratio and inhibiting Caspase-3 pathway.
Keywords: Bak Foong Pills; Bcl-2/Bax; Caspase-3 mRNA; optic nerve damage; β-amyloid protein.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rat retinal ganglion cells upregulate the pro-apoptotic BH3-only protein Bim after optic nerve transection.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2003 Dec 12;120(1):30-7. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2003.09.016. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2003. PMID: 14667574
-
Ganoderma spore lipid inhibits N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced retinal photoreceptor apoptosis in vivo.Exp Eye Res. 2010 Mar;90(3):397-404. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2009.11.017. Epub 2009 Dec 7. Exp Eye Res. 2010. PMID: 20003911
-
[Study of the mechanisms of curcumin on mitochondrial permeability transition of hepatocytes in rats with sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014 Sep;26(9):666-70. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2014.09.012. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014. PMID: 25230870 Chinese.
-
[Effect of Active Ingredients of Qingxin Kaiqiao Recipe on Spatial Learning and Memory Capacities, and Expressions of Bax, Bcl-2, Caspase-3, and PAPP in Hippocampus of AD Model Rats].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2017 Feb;37(2):189-197. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 30650272 Chinese.
-
Correlations of SDF-1 and CXCR4 levels with caspase-3 expression in the retina of rats after optic nerve injury.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020 Aug 1;13(8):2058-2064. eCollection 2020. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32922601 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
BACE1 Inhibition Increases Susceptibility to Oxidative Stress by Promoting Mitochondrial Damage.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Sep 28;10(10):1539. doi: 10.3390/antiox10101539. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34679674 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parrilla-Reverter G, Agudo M, Sobrado-Calvo P, Salinas-Navarro M, Villegas-Perez MP, Vidal-Sanz M. Effects of different neurotrophic factors on the survival of retinal ganglion cells after a complete intraorbital nerve crush injury: a quantitative in vivo study. Exp Eye Res. 2009;89(1):32–41. - PubMed
-
- Jellinger KA. Recent advances in our understanding of neurodegeneration. J Neural Transm. 2009;116(9):1111–1162. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials