Bis(7)-tacrine protects retinal ganglion cells against excitotoxicity via NMDA receptor inhibition
- PMID: 22553626
- PMCID: PMC3340694
- DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2011.02.03
Bis(7)-tacrine protects retinal ganglion cells against excitotoxicity via NMDA receptor inhibition
Abstract
Aim: To investigate whether bis(7)-tacrine, a multifunctional drug, inhibits N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) -activated current in retinal ganglion cells(RGC) and provides neuroprotection against retinal cell damage.
Methods: Purified RGC cultures were obtained from retinas of 1-3 days old Sprague-Dawley(SD) rats, following a two-step immunopanning procedure. After 7 days of cultivation, the inhibition of NMDA-activated current by bis(7)-tacrine was measured by using patch-clamp recording techniques. In animal experiments, RGCs were damaged after intravitreal injection of NMDA (5µL, 40nmol) in adult rats. Bis(7)-tacrine(0.05, 0.1, 0.2mg/kg) or memantine(20mg/kg) was intraperitoneal administered to the rats fifteen minutes before intravitreally injection of NMDA. RGC damage was analyzed by histologic techniques, TUNEL and retrograde labeling techniques.
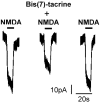
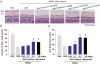
Results: Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings demonstrated that NMDA (30µmol/L) resulted in approximately -50 pA inward currents that were blocked by bis(7)-tacrine(1µmol/L). Histological examination and retrograde labeling analysis revealed that bis(7)-tacrine induced a significant neuroprotective effect against NMDA-induced cell damage 7 days after NMDA injection. TUNEL staining showed that pretreatment with bis(7)-tacrine was effective in ameliorating NMDA-induced apoptotic cell loss in the retinal ganglion cell layer 18 hours after injection.
Conclusion: Bis(7)-tacrine possesses remarkable neuroprotective activities against retinal excitotoxicity through inhibition of NMDA receptors.
Keywords: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors; bis(7)-tacrine; excitotoxicity; neuroprotection.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effects of bis(7)-tacrine against glutamate-induced retinal ganglion cells damage.BMC Neurosci. 2010 Mar 3;11:31. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-11-31. BMC Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20199668 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Effect of Magnesium Acetyltaurate Against NMDA-Induced Excitotoxicity in Rat Retina.Neurotox Res. 2017 Jan;31(1):31-45. doi: 10.1007/s12640-016-9658-9. Epub 2016 Aug 27. Neurotox Res. 2017. PMID: 27568334
-
Novel dimeric acetylcholinesterase inhibitor bis7-tacrine, but not donepezil, prevents glutamate-induced neuronal apoptosis by blocking N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors.J Biol Chem. 2005 May 6;280(18):18179-88. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M411085200. Epub 2005 Feb 14. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15710623
-
Inhibition of NMDA-gated ion channels by bis(7)-tacrine: whole-cell and single-channel studies.Neuropharmacology. 2008 Jun;54(7):1086-94. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.02.015. Epub 2008 Mar 2. Neuropharmacology. 2008. PMID: 18407299
-
Alpha2 adrenergic modulation of NMDA receptor function as a major mechanism of RGC protection in experimental glaucoma and retinal excitotoxicity.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008 Oct;49(10):4515-22. doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-2078. Epub 2008 Jun 19. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18566471
Cited by
-
Antioxidant drug therapy approaches for neuroprotection in chronic diseases of the retina.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Jan 27;15(2):1865-86. doi: 10.3390/ijms15021865. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24473138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Small Organic Compound Mimicking the L1 Cell Adhesion Molecule Promotes Functional Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury in Zebrafish.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Jan;55(1):859-878. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0254-z. Epub 2017 Jan 9. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28070857
-
Rationale for the use of multifunctional drugs as neuroprotective agents for glaucoma.Neural Regen Res. 2012 Feb 5;7(4):313-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.04.013. Neural Regen Res. 2012. PMID: 25806075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Targets of Bis (7)-Cognitin and Its Relevance in Neurological Disorders: A Systematic Review.Front Neurosci. 2019 May 9;13:445. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00445. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31143096 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Casson RJ. Possible role of excitotoxicity in the pathogenesis of glaucoma. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2006;34(1):54–63. - PubMed
-
- Gilling KE, Jatzke C, Hechenberger M, Parsons CG. Potency, voltage-dependency, agonist concentration-dependency, blocking kinetics and partial untrapping of the uncompetitive N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) channel blocker memantine at human NMDA (GluN1/GluN2A) receptors. Neuropharmacology. 2009;56(5):866–875. - PubMed
-
- Osborne NN. Recent clinical findings with memantine should not mean that the idea of neuroprotection in glaucoma is abandoned. Acta Ophthalmol. 2009;87(4):450–454. - PubMed
-
- Danesh-Meyer HV, Levin LA. Neuroprotection: extrapolating from neurologic diseases to the eye. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009;148(2):186–191. - PubMed
-
- Fu H, Li W, Luo J, Lee NT, Li M, Tsim KW, Pang Y, Youdim MB, Han Y. Promising anti-Alzheimer's dimer bis(7)-tacrine reduces beta-amyloid generation by directly inhibiting BACE-1 activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;366(3):631–636. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
