Expressions of cellular retinoic acid binding proteins I and retinoic acid receptor-β in the guinea pig eyes with experimental myopia
- PMID: 22553627
- PMCID: PMC3340703
- DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2011.02.04
Expressions of cellular retinoic acid binding proteins I and retinoic acid receptor-β in the guinea pig eyes with experimental myopia
Abstract
Aim: All-trans retinoic acid (RA) is the only extrinsic biochemical candidate known to date that could act as a growth controller, the aim of this study was to investigate the expression cellular retinoic acid binding proteins I (CRABP-I) and retinoic acid receptor-β (RAR-β) in retina of the guinea pig eyes with experimental myopia.
Methods: Ninety guinea pigs aged 14 days were equally and randomly divided into three groups: form deprivation (FD), -5D lens, and control. The diffusers for FD were white translucent hemispheres, and -5D lenses were used to introduce hyperopic defocus. Refraction was measured with streak retinoscopy after cycloplegia, and axial length was calculated with Cinescan A/B ultrasonography. Retina harvested at different time points were used to measure RA level with HPLC and expressions of cellular retinoic acid binding proteins I (CRABP-I) and RA receptor-β (RAR-β) were assayed with Western blot and Real-time PCR. SPSS13.0 software was used for statistical analysis.
Results: Up-regulations of CRABP-I and RAR-β in ocular tissues correlated with changes in the refractive status and growth rate of the guinea pig eye (P<0.05). 14 days of monocular form-deprivation led to -5.14D myopia and a 0.281mm axial elongation; 14 days of monocular defocus produced -3.64D myopia and a 0.163 mm axial elongation. The level of retinal RA started to elevate in 7 days (P<0.05) after visual manipulation in both FD and -5D lens groups and became more prominent by 14 days (P<0.01) . The expressions of CRABP-I and RAR-β increased by 14 days after visual manipulation (P<0.05), the mRNA level of RAR-β, however, increased by 7 days after visual manipulation (P<0.05), which suggested that changes of expressions of CRABP-I and RAR-β might lag behind the change of RA.
Conclusion: The levels of CRABP-I and RAR-β were elevated in retina of the guinea pig eye with experimental myopia. During the progression of experimental myopia, the retinal RA level increased rapidly, and there might be a positive feedback between the increase of RA and up-regulation of RAR-β.
Keywords: CRABP-I; RAR-β; experimental myopia; guinea pig; retinoic acid.
Figures

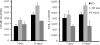
References
-
- Schaeffel F, Diether S. The growing eye: an autofocus system that works on very poor images. Vision Res. 1999;39:1585–1589. - PubMed
-
- Wallman J, Winawer J. Homeostasis of eye growth and the question of myopia. Neuron. 2004;43:447–468. - PubMed
-
- Wiesel TN, Raviola E. Myopia and eye enlargement after neonatal lid fusion in monkeys. Nature. 1977;266:66–68. - PubMed
-
- Venkataraman S, Nguyen L, McBrien NA. Compensatory ocular growth responses to positive lens defocus in the tree shrew. Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005;46:E-Abstract 1973.
-
- Howlett MC, McFadden SA. A fast and effective mammalian model to study the visual regulation of growth. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002;43:2928.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
