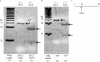
Validation of PCR for the detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from corneal samples
- PMID: 22553658
- PMCID: PMC3340821
- DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2011.03.10
Validation of PCR for the detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from corneal samples
Abstract
Aim: To determine a species-specific real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay to detect Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA), a secondary DNA target for PA that may provide a universal target for other bacterial pathogens, and validate both assays for diagnostic testing.
Methods: PCR detection was established against the ecfX PA gene and the 16S rRNA gene using known PA keratitis isolates. The outcome parameters for both assays were "limit of detection" (LOD), amplification efficiency (AE), and PAGE amplified product analysis. Both assays were validated against 20 true-positive clinical samples positive for PA DNA and 20 true-negative samples containing no PA DNA. Descriptive statistics and PAGE analysis were used as outcome parameters.
Results: AE of the ecfX assay was 96.6%, and LOD was 33.6 copies of target DNA per microliter. AE of the 16S rRNA assay was 103.4%, and LOD was 8.12 copies per microliter. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and efficiency for the ecfX and 16S rRNA assays were [75%, 95%, 94%, 79%, and 85%], and [70%, 100%, 100%, 77%, and 85%], respectively. Both PCR assays were validated, followed by confirmation of DNA patterns from PAGE analysis.
Conclusion: The PCR methodology described here may be a useful adjunct to standard methods in the diagnosis of PA keratitis.
Keywords: 16S rRNA; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; cornea; ecfX; real-time PCR.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[A broad-range 16S rRNA gene real-time PCR assay for the diagnosis of neonatal septicemia].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2007 Jun;45(6):446-9. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 17880793 Chinese.
-
[Rapid detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by the fluorescence quantitative PCR assay targeting 16S rDNA].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2006 Sep;22(5):789-94. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2006. PMID: 17037203 Chinese.
-
Comparison of a new quantitative ompA-based real-Time PCR TaqMan assay for detection of Chlamydia pneumoniae DNA in respiratory specimens with four conventional PCR assays.J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Feb;41(2):592-600. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.2.592-600.2003. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12574252 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by a duplex real-time polymerase chain reaction assay targeting the ecfX and the gyrB genes.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009 Feb;63(2):127-31. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2008.09.018. Epub 2008 Nov 21. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19026507
-
[Application of recombinase polymerase amplification in the detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2018 Apr 20;34(4):233-239. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2018.04.008. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29690742 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Detection of bacterial 16S rRNA and identification of four clinically important bacteria by real-time PCR.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48558. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048558. Epub 2012 Nov 6. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23139793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Choy M H, Stapleton F, Willcox M D, Zhu H. Comparison of virulence factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from contact lens- and non-contact lens-related keratitis. J Med Microbiol. 2008;57:1539–1546. - PubMed
-
- Huang AJW, Wichiensin P, Yang MC. Bacterial Keraitis. In: Krachmer J H, Mannis M J, Holland E J, editors. Cornea. 2nd Ed. Vol 1. Elsevier Mosby; 2004. p. 1005.
-
- Wilhelmus K R. Indecision about corticosteroids for bacterial keratitis: an evidence-based update. Ophthalmology. 2002;109:835–842. - PubMed
-
- Lavenir R, Jocktane D, Laurent F, Nazaret S, Cournoyer B. Improved reliability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PCR detection by the use of the species-specific ecfX gene target. J Microbiol Methods. 2007;70:20–29. - PubMed
-
- Anuj S N, Whiley D M, Kidd T J, Bell S C, Wainwright C E, Nissen M D, Sloots T P. Identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by a duplex real-time polymerase chain reaction assay targeting the ecfX and the gyrB genes. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009;63:127–131. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources