Investigation of immunogenicity of cryopreserved limbal stem cells
- PMID: 22553726
- PMCID: PMC3340795
- DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2011.06.03
Investigation of immunogenicity of cryopreserved limbal stem cells
Abstract
Aim: To investigate changes in immunogenicity of cryopreserved limbal stem cells.
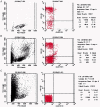
Methods: Cryopreserved limbal stem cells, fresh primary limbal stem cells and blank controls were inoculated subcutaneously in C57BL-6 mice and the percentage of CD25 cells in limbal explants was determined by flow cytometry at day 21 post inoculation. Morphological studies were performed by light and electron microscopy of limbal explant sections.
Results: The number of regional and systemic lymphocytes derived from cryopreserved limbal stem cells was lower than that from fresh primary limbal stem cells.
Conclusion: Lymphocytes derived from cryopreserved limbal stem cells showed changes in immunogenicity, but the significance is unknown. The cryopreservation and thawing methods await further study.
Keywords: cryopreservation; explant; immunogenicity; rabbit limbal stem cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cultivation and phenotypic characterization of rabbit epithelial cells expanded ex vivo from fresh and cryopreserved limbal and oral mucosal explants.Curr Eye Res. 2015 Mar;40(3):274-81. doi: 10.3109/02713683.2014.917191. Epub 2014 May 15. Curr Eye Res. 2015. PMID: 24833207
-
Limbal explants from cryopreserved cadaver human corneas. Immunofluorescence and light microscopy of epithelial cells growing in culture.Cryo Letters. 2009 May-Jun;30(3):183-9. Cryo Letters. 2009. PMID: 19750242
-
[An experimental study on limbal stem cells autograft transplantation with cryopreservation].Yan Ke Xue Bao. 1998 Dec;14(4):224-6, 231. Yan Ke Xue Bao. 1998. PMID: 12579742 Chinese.
-
Has allogeneic stem cell cryopreservation been given the 'cold shoulder'? An analysis of the pros and cons of using frozen versus fresh stem cell products in allogeneic stem cell transplantation.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2006 Sep;38(6):399-405. doi: 10.1038/sj.bmt.1705462. Epub 2006 Aug 7. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2006. PMID: 16892075 Review.
-
Cryopreservation of Hair-Follicle Associated Pluripotent (HAP) Stem Cells Maintains Differentiation and Hair-Growth Potential.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;951:191-198. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-45457-3_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27837565 Review.
References
-
- Bratanov M, Neronov A, Nikolova E. Limbal explants from cryop-reserved cadaver human corneas.Immunofluorescence and light microscopy of epithelial cells growing in culture. Croy letters. 2009;30:183–189. - PubMed
-
- Gao MH, Zhang JS, Lan P. Viability of the rabbits'corneal limbal epithelial cells cryopreserved at -196°C. Chinese Journal of Practical Ophthalmology. 2006;24:658–661.
-
- Yeh HJ, Yao CL, Chen HI. Cryopreservation of human Iimbal stem cells ex vivo expanded on amniotic membrane. Cornea. 2008;27:327–333. - PubMed
-
- Zhou SB, Chen JQ, Huang T, Chen LS, Xu LY. A experimental study on limbal stem cells viability with cryopreservation. Chongqing Medical Journal. 2000;29:481–482.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
