Inhibited experimental corneal neovascularization by neutralizing anti-SDF-1α antibody
- PMID: 22553746
- PMCID: PMC3340834
- DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2012.01.02
Inhibited experimental corneal neovascularization by neutralizing anti-SDF-1α antibody
Abstract
Aim: To explore the effect of SDF-1α on the development of experimental corneal neovascularization (CRNV).
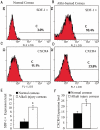
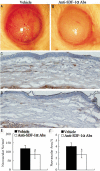
Methods: CRNV was induced by alkali injury in mice. The expression of SDF-1α and CXCR4 in burned corneas was examined by Flow Cytometry. Neutralizing anti-mouse SDF-1α antibody was locally administrated after alkali injury and the formation of CRNV 2 weeks after injury was assessed by Immunohistochemistry. The expression of VEGF and C-Kit in burned corneas was detected by RT-PCR.
Results: The number of CRNV peaks at 2 weeks after alkali injury. Compared to control group, SDF-1α neutralizing antibody treatment significantly decreased the number of CRNV. RT-PCR confirmed that SDF-1α neutralizing antibody treatment resulted in decreased intracorneal VEGF and C-Kit expression.
Conclusion: SDF-1α neutralizing antibody treated mice exhibited impaired experimental CRNV through down regulated VEGF and C-Kit expression.
Keywords: alkali injury; chemokine; corneal neovascularization.
Figures
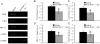
References
-
- Ambati BK, Nozaki M, Singh N, Takeda A, Jani PD, Suthar T, Albuquerque RJ, Richter E, Sakurai E, Newcomb MT, Kleinman ME, Caldwell RB, Lin Q, Ogura Y, Orecchia A, Samuelson DA, Agnew DW, St Leger J, Green WR, Mahasreshti PJ, Curiel DT, Kwan D, Marsh H, Ikeda S, Leiper LJ, Collinson JM, Bogdanovich S, Khurana TS, Shibuya M, Baldwin ME, Ferrara N, Gerber HP, De Falco S, Witta J, Baffi JZ, Raisler BJ, Ambati J. Corneal avascularity is due to soluble VEGF receptor-1. Nature. 2006;443:993–997. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang S, Ma J. Ocular neovascularization: Implication of endogenous angiogenic inhibitors and potential therapy. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2007;26:1–37. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
