Individualized reduction in dialysate sodium in conventional in-center hemodialysis
- PMID: 22554224
- PMCID: PMC3660723
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1542-4758.2012.00701.x
Individualized reduction in dialysate sodium in conventional in-center hemodialysis
Abstract
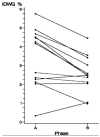
Recent studies have focused on the association between dialysate sodium (Na(+)) prescriptions and interdialytic weight gain (IDWG). We report on a case series of 13 patients undergoing conventional, thrice-weekly in-center hemodialysis with an individualized dialysate Na(+) prescription. Individualized dialysate Na(+) was achieved in all patients through a stepwise weekly reduction of the standard dialysate Na(+) prescription (140 mEq/L) by 2-3 mEq/L until reaching a Na(+) gradient of -2 mEq/L (dialysate Na(+) minus average plasma Na(+) over the preceding 3 months). Interdialytic weight gain, with and without indexing to dry weight (IDWG%), blood pressure, and the proportion of treatments with cramps, intradialytic hypotension (drop in systolic blood pressure >30 mmHg) and intradialytic hypotension requiring an intervention were reviewed. At the beginning of the observation period, the pre-hemodialysis (HD) plasma Na(+) concentration ranged from 130 to 141 mEq/L. When switched from the standard to the individualized dialysate Na(+) concentration, IDWG% decreased from 3.4% ± 1.6% to 2.5% ± 1.0% (P = 0.003) with no change in pre- or post-HD systolic or diastolic blood pressures (all P > 0.05). We found no significant change in the proportion of treatments with cramps (6% vs. 13%), intradialytic hypotension (62% vs. 65%), or intradialytic hypotension requiring an intervention (29% vs. 33%). Individualized reduction of dialysate Na(+) reduces IDWG% without significantly increasing the frequency of cramps or hypotension.
© 2012 The Authors. Hemodialysis International © 2012 International Society for Hemodialysis.
Figures
References
-
- Ok E, Mees EJ. Unpleasant truths about salt restriction. Semin Dial. 2010;23:1–3. - PubMed
-
- Penne EL, Levin NW, Kotanko P. Improving volume status by comprehensive dietary and dialytic sodium management in chronic hemodialysis patients. Blood Purif. 2010;30:71–78. - PubMed
-
- de Paula FM, Peixoto AJ, Pinto LV, Dorigo D, Patricio PJ, Santos SF. Clinical consequences of an individualized dialysate sodium prescription in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2004;66:1232–1238. - PubMed
-
- Flanigan MJ. How should dialysis fluid be Individualized for the chronic hemodialysis patient? Sodium. Semin Dial. 2008;21:226–229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical