Isolation of antibacterial compounds from Quercus dilatata L. through bioassay guided fractionation
- PMID: 22554280
- PMCID: PMC3416653
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-0711-11-11
Isolation of antibacterial compounds from Quercus dilatata L. through bioassay guided fractionation
Abstract
Background: Four medicinal plants (Chrozophora hierosolymitana Spreng, Chrysanthemum leucanthemum L., Ephedra gerardiana Wall. ex Stapf, and Quercus dilatata L.) used by indigenous healers to treat various infectious diseases were selected for the present study. The major objective of the present study was isolation and characterization of antimicrobial components from the crude plant extracts using bioassay guided fractionation.
Methods: Seven methanolic extracts of the four plants were screened to identify any antimicrobial agents present in them. The active crude plant extract was fractionated first by solvent partitioning and then by HPLC. Characterization of the active fractions was done by using spectrophotometer.
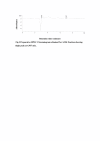
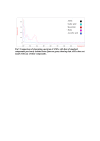
Results: All the seven methanolic extracts showed low antifungal activity, however, when these extracts were tested for antibacterial activity, significant activity was exhibited by two extracts. The extract of aerial parts of Q. dilatata was most active and therefore, was selected for further analysis. Initially fractionation was done by solvent-solvent partitioning and out of six partitioned fractions, ethanol fraction was selected on the basis of results of antibacterial activity and phytochemical analysis. Further, fractionation was carried out by RP-HPLC and purified active subfractions were characterized by comparing their absorption spectra with that of the known natural products isolated from the plants of Quercus genus.
Discussion and conclusion: The results suggest that this is the first report of the isolated antibacterial compounds from this genus.
Figures



References
-
- Malheiros A, Filho VC, Schmitt CB, Yunes RA, Escalante A, Svetaz L, Zacchino S, Monache FD. Antifungal activity of drimane sesquiterpenes from Drimys brasiliensis using bioassay-guided fractionation. J Pharm Pharmaceut Sci. 2005;8:335–339. - PubMed
-
- Harraz FM, Abdel-Aziz SA. Chemical and biological studies of Chrozophora verbascifolia. Zagazig J Pharm Sci. 1994;3:72–78.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

