Gene expression pattern of the epidermal growth factor receptor family and LRIG1 in renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 22554477
- PMCID: PMC3419632
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-5-216
Gene expression pattern of the epidermal growth factor receptor family and LRIG1 in renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have revealed altered expression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-family members and their endogenous inhibitor leucine-rich and immunoglobulin-like domains 1 (LRIG1) in renal cell carcinoma (RCC). In this study, we analyzed the gene expression levels of EGFR-family members and LRIG1, and their possible associations with clinical parameters in various types of RCC.
Methods: Gene expression levels of EGFR-family members and LRIG1 were analyzed in 104 RCC samples, including 81 clear cell RCC (ccRCC), 15 papillary RCC (pRCC), and 7 chromophobe RCC (chRCC) by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Associations between gene expression levels and clinical data, including tumor grade, stage, and patient survival were statistically assessed.
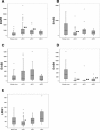
Results: Compared to kidney cortex, EGFR was up-regulated in ccRCC and pRCC, LRIG1 and ERBB2 were down-regulated in ccRCC, and ERBB4 was strongly down-regulated in all RCC types. ERBB3 expression did not differ between RCC types or between RCC and the kidney cortex. The expression of the analyzed genes did not correlate with patient outcome.
Conclusions: This study revealed that the previously described up-regulation of EGFR and down-regulation of ERBB4 occurred in all analyzed RCC types, whereas down-regulation of ERBB2 and LRIG1 was only present in ccRCC. These observations illustrate the need to evaluate the different RCC types individually when analyzing molecules of interest and potential biological markers.
Figures
References
-
- Störkel S, Eble J, Adlakha K, Amin M, Blute M, Bostwick D, Darson M, Delahunt B, Iczkowski K. Classification of renal cell carcinoma: Workgroup No. 1. Union Internationale Contre le Cancer (UICC) and the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) Cancer. 1997;80:987–989. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19970901)80:5<987::AID-CNCR24>3.0.CO;2-R. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baldewijns MM, van Vlodrop IJ, Schouten LJ, Soetekouw PM, de Bruine AP, van Engeland M. Genetics and epigenetics of renal cell cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1785:133–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

