Small-animal imaging using clinical positron emission tomography/computed tomography and super-resolution
- PMID: 22554485
- PMCID: PMC3694434
Small-animal imaging using clinical positron emission tomography/computed tomography and super-resolution
Abstract
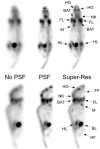
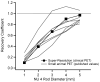
Considering the high cost of dedicated small-animal positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT), an acceptable alternative in many situations might be clinical PET/CT. However, spatial resolution and image quality are of concern. The utility of clinical PET/CT for small-animal research and image quality improvements from super-resolution (spatial subsampling) were investigated. National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) NU 4 phantom and mouse data were acquired with a clinical PET/CT scanner, as both conventional static and stepped scans. Static scans were reconstructed with and without point spread function (PSF) modeling. Stepped images were postprocessed with iterative deconvolution to produce super-resolution images. Image quality was markedly improved using the super-resolution technique, avoiding certain artifacts produced by PSF modeling. The 2 mm rod of the NU 4 phantom was visualized with high contrast, and the major structures of the mouse were well resolved. Although not a perfect substitute for a state-of-the-art small-animal PET/CT scanner, a clinical PET/CT scanner with super-resolution produces acceptable small-animal image quality for many preclinical research studies.
Figures



References
-
- Chatziioannou AF. Molecular imaging of small animals with dedicated PET tomographs. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002;29:98–114. - PubMed
-
- Vanderheyden JL. The use of imaging in preclinical drug development. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009;53:374–81. - PubMed
-
- Chatziioannou AF. PET scanners dedicated to molecular imaging of small animal models. Mol Imaging Biol. 2002;4:47–63. - PubMed
-
- Levin CS, Zaidi H. Current trends in preclinical PET system design. PET Clin. 2007;2:125–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
