Orexin 1 receptors are a novel target to modulate panic responses and the panic brain network
- PMID: 22554617
- PMCID: PMC3472124
- DOI: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2012.04.016
Orexin 1 receptors are a novel target to modulate panic responses and the panic brain network
Abstract
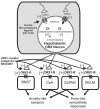
Background: Although the hypothalamic orexin system is known to regulate appetitive behaviors and promote wakefulness and arousal (Sakurai, 2007 [56]), this system may also be important in adaptive and pathological anxiety/stress responses (Suzuki et al., 2005 [4]). In a recent study, we demonstrated that CSF orexin levels were significantly higher in patients experiencing panic attacks compared to non-panicking depressed subjects (Johnson et al., 2010 [9]). Furthermore, genetically silencing orexin synthesis or blocking orexin 1 receptors attenuated lactate-induced panic in an animal model of panic disorder. Therefore, in the present study, we tested if orexin (ORX) modulates panic responses and brain pathways activated by two different panicogenic drugs.
Methods: We conducted a series of pharmacological, behavioral, physiological and immunohistochemical experiments to study the modulation by the orexinergic inputs of anxiety behaviors, autonomic responses, and activation of brain pathways elicited by systemic injections of anxiogenic/panicogenic drugs in rats.
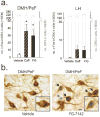
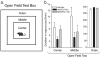
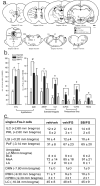
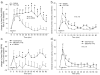
Results: We show that systemic injections of two different anxiogenic/panicogenic drugs (FG-7142, an inverse agonist at the benzodiazepine site of the GABA(A) receptor, and caffeine, a nonselective competitive adenosine receptor antagonist) increased c-Fos induction in a specific subset of orexin neurons located in the dorsomedial/perifornical (DMH/PeF) but not the lateral hypothalamus. Pretreating rats with an orexin 1 receptor antagonist attenuated the FG-7142-induced anxiety-like behaviors, increased heart rate, and neuronal activation in key panic pathways, including subregions of the central nucleus of the amygdala, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, periaqueductal gray and in the rostroventrolateral medulla.
Conclusion: Overall, the data here suggest that the ORX neurons in the DMH/PeF region are critical to eliciting coordinated panic responses and that ORX1 receptor antagonists constitute a potential novel treatment strategy for panic and related anxiety disorders. The neural pathways through which ORX1 receptor antagonists attenuate panic responses involve the extended amygdala, periaqueductal gray, and medullary autonomic centers.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Sakurai T, Amemiya A, Ishii M, Matsuzaki I, Chemelli RM, Tanaka H, et al. Orexins and orexin receptors: a family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell. 1998;92:573–85. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki M, Beuckmann CT, Shikata K, Ogura H, Sawai T. Orexin-A (hypocretin-1) is possibly involved in generation of anxiety-like behavior. Brain Res. 2005;1044:116–21. - PubMed
-
- Samson WK, Taylor MM, Follwell M, Ferguson AV. Orexin actions in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus: physiological consequences and cellular correlates. Regul Pept. 2002;104:97–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

