Expression of the Wnt antagonist Dickkopf-3 is associated with prognostic clinicopathologic characteristics and impairs proliferation and invasion in endometrial cancer
- PMID: 22555103
- PMCID: PMC3688285
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2012.04.026
Expression of the Wnt antagonist Dickkopf-3 is associated with prognostic clinicopathologic characteristics and impairs proliferation and invasion in endometrial cancer
Abstract
Objective: Emerging evidence implicates the Wnt antagonist Dickkopf-3 (Dkk3) as a tumor suppressor and potential biomarker in solid tumors. We investigated whether Dkk3 plays an important role in the carcinogenesis of endometrial cancer (EC).
Methods: We analyzed Dkk3 mRNA expression via real-time RT-PCR in twenty-seven human primary EC tissues, and six matched normal endometrial controls. Dkk3 levels were correlated with various clinicopathologic characteristics. Additionally, enforced Dkk3 expression was examined in proliferation and tumorigenesis in vitro and in vivo, using MTT, soft agar assay, invasion assay, a xenograft mouse model, and a β-catenin-responsive SuperTopFlash luciferase assay.
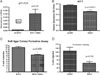
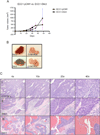
Results: Compared with matched normal endometrial cases, Dkk3 was down-regulated in EC (p<0.0001). Among cancer cases, Dkk3 expression was significantly reduced in patients with higher stage (p=0.002), positive pelvic lymph nodes (p=0.0004), non-endometrioid histology (p=0.02), and cytology-positive ECs (p=0.02). Enforced expression of Dkk3 in EC cell lines showed reduced proliferation (p<0.0001), anchorage-independent growth (p=0.005), invasion (p=0.02), and reduced TCF activity (p=0.04), confirming Dkk3 as a negative regulator of the β-catenin/Wnt signaling pathway. Tumor growth in Dkk3-injected mice was not statistically different, though did plateau towards the end, and was associated with increased lymphoid infiltration and tumor necrosis.
Conclusion: Dkk3 gene expression is frequently downregulated in endometrial cancer, and is associated with poor prognostic clinicopathologic markers. The results also identify a role for Dkk3 as a tumor suppressor in EC, affecting both proliferation and invasiveness. These findings may prove to be important in the design of novel biomarkers and treatment modalities for advanced EC.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial disclosures or conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Epigenetic silencing of the WNT antagonist Dickkopf 3 disrupts normal Wnt/β-catenin signalling and apoptosis regulation in breast cancer cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2013 Oct;17(10):1236-46. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12099. Epub 2013 Jul 24. J Cell Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23890219 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Patterns of the Wnt Pathway Inhibitors Dickkopf3 and Secreted Frizzled-Related Proteins 1 and 4 in Endometrial Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma: An NRG Oncology/Gynecologic Oncology Group Study.Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2016 Jan;26(1):125-32. doi: 10.1097/IGC.0000000000000563. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26397159 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Wnt signalling in human breast cancer: expression of the putative Wnt inhibitor Dickkopf-3 (DKK3) is frequently suppressed by promoter hypermethylation in mammary tumours.Breast Cancer Res. 2008;10(5):R82. doi: 10.1186/bcr2151. Epub 2008 Sep 30. Breast Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18826564 Free PMC article.
-
Dickkopf homolog 3 (DKK3): A candidate for detection and treatment of cancers?J Cell Physiol. 2018 Jun;233(6):4595-4605. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26313. Epub 2018 Jan 15. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29206297 Review.
-
DKK3 expression and function in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and other cancers.J Oral Biosci. 2020 Mar;62(1):9-15. doi: 10.1016/j.job.2020.01.008. Epub 2020 Feb 4. J Oral Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32032750 Review.
Cited by
-
Dickkopf-3 Causes Neuroprotection by Inducing Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Sep 11;12:292. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00292. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30258353 Free PMC article.
-
BD-Func: a streamlined algorithm for predicting activation and inhibition of pathways.PeerJ. 2013 Sep 12;1:e159. doi: 10.7717/peerj.159. eCollection 2013. PeerJ. 2013. PMID: 24058887 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterisation of Canine Osteosarcoma in High Risk Breeds.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 25;12(9):2405. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092405. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32854182 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic silencing of the WNT antagonist Dickkopf 3 disrupts normal Wnt/β-catenin signalling and apoptosis regulation in breast cancer cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2013 Oct;17(10):1236-46. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12099. Epub 2013 Jul 24. J Cell Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23890219 Free PMC article.
-
Dkk3 prevents familial dilated cardiomyopathy development through Wnt pathway.Lab Invest. 2016 Feb;96(2):239-48. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2015.145. Epub 2015 Dec 7. Lab Invest. 2016. PMID: 26641069
References
-
- Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(4):212–236. - PubMed
-
- Bokhman JV. Two pathogenetic types of endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 1983;15(1):10–17. - PubMed
-
- Obel JC, Friberg G, Fleming GF. Chemotherapy in endometrial cancer. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2006;4(6):459–468. - PubMed
-
- Dellinger TH, Monk BJ. Systemic therapy for recurrent endometrial cancer: a review of North American trials. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2009;9(7):905–916. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U10 CA027469/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA122558/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 CA082450/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA060396/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA062203/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA152804/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA071789/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 2T32 CA-060396-11/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K24CA82450/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA37517/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK065642/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA27469/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037517/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA11479/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States

