A non-exercise testing method for estimating cardiorespiratory fitness: associations with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in a pooled analysis of eight population-based cohorts
- PMID: 22555215
- PMCID: PMC3590456
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs097
A non-exercise testing method for estimating cardiorespiratory fitness: associations with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in a pooled analysis of eight population-based cohorts
Abstract
Aims: Cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) is a key predictor of chronic disease, particularly cardiovascular disease (CVD), but its assessment usually requires exercise testing which is impractical and costly in most health-care settings. Non-exercise testing cardiorespiratory fitness (NET-F)-estimating methods are a less resource-demanding alternative, but their predictive capacity for CVD and total mortality has yet to be tested. The objective of this study is to examine the association of a validated NET-F algorithm with all-cause and CVD mortality.
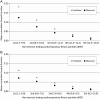
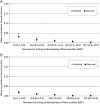
Methods and results: The participants were 32,319 adults (14,650 men) aged 35-70 years who took part in eight Health Survey for England and Scottish Health Survey studies between 1994 and 2003. Non-exercise testing cardiorespiratory fitness (a metabolic equivalent of VO2max) was calculated using age, sex, body mass index (BMI), resting heart rate, and self-reported physical activity. We followed participants for mortality until 2008. Two thousand one hundred and sixty-five participants died (460 cardiovascular deaths) during a mean 9.0 [standard deviation (SD) = 3.6] year follow-up. After adjusting for potential confounders including diabetes, hypertension, smoking, social class, alcohol, and depression, a higher fitness score according to the NET-F was associated with a lower risk of mortality from all-causes (hazard ratio per SD increase in NET-F 0.85, 95% confidence interval: 0.78-0.93 in men; 0.88, 0.80-0.98 in women) and CVD (men: 0.75, 0.63-0.90; women: 0.73, 0.60-0.92). Non-exercise testing cardiorespiratory fitness had a better discriminative ability than any of its components (CVD mortality c-statistic: NET-F = 0.70-0.74; BMI = 0.45-0.59; physical activity = 0.60-0.64; resting heart rate = 0.57-0.61). The sensitivity of the NET-F algorithm to predict events occurring in the highest risk quintile was better for CVD (0.49 in both sexes) than all-cause mortality (0.44 and 0.40 for men and women, respectively). The specificity for all-cause and CVD mortality ranged between 0.80 and 0.82. The net reclassification improvement of CVD mortality risk (vs. a standardized aggregate score of the modifiable components of NET-F) was 27.2 and 21.0% for men and women, respectively.
Conclusion: The CRF-estimating method NET-F that does not involve exercise testing showed consistent associations with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality, and it had good discrimination and excellent risk reclassification improvement. As such, it merits further attention as a practical and potentially and useful risk prediction tool.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Longitudinal algorithms to estimate cardiorespiratory fitness: associations with nonfatal cardiovascular disease and disease-specific mortality.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014 Jun 3;63(21):2289-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.03.008. Epub 2014 Apr 2. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24703924 Free PMC article.
-
Heart rate reserve as a predictor of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in men.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002 Dec;34(12):1873-8. doi: 10.1097/00005768-200212000-00003. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002. PMID: 12471290
-
Long-term effects of changes in cardiorespiratory fitness and body mass index on all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality in men: the Aerobics Center Longitudinal Study.Circulation. 2011 Dec 6;124(23):2483-90. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.038422. Circulation. 2011. PMID: 22144631 Free PMC article.
-
Survival of the Fittest: Impact of Cardiorespiratory Fitness on Outcomes in Men and Women with Cardiovascular Disease.Clin Ther. 2020 Mar;42(3):385-392. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2020.01.014. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Clin Ther. 2020. PMID: 32088022 Review.
-
Comparison of objectively measured and estimated cardiorespiratory fitness to predict all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 42 studies representing 35 cohorts and 3.8 million observations.J Sport Health Sci. 2024 Sep 11;14:100986. doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2024.100986. Online ahead of print. J Sport Health Sci. 2024. PMID: 39271056 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Non-exercise estimated cardiorespiratory fitness and cancer incidence: The NIH-AARP diet and health study.J Sport Health Sci. 2023 Nov;12(6):739-746. doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2023.02.004. Epub 2023 Feb 23. J Sport Health Sci. 2023. PMID: 36828228 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of Non-Exercise Estimated Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Japanese Adults.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Nov 23;18(23):12288. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182312288. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34886012 Free PMC article.
-
Is cardiorespiratory fitness associated with cognitive outcomes in mid-adulthood? Findings from the 1958 British birth cohort.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2023 Dec;33(12):2613-2619. doi: 10.1111/sms.14525. Epub 2023 Oct 18. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2023. PMID: 37853511 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiorespiratory fitness mediates the effects of aging on cerebral blood flow.Front Aging Neurosci. 2014 Apr 7;6:59. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2014.00059. eCollection 2014. Front Aging Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24778617 Free PMC article.
-
Validity of Cardiorespiratory Fitness Measured with Fitbit Compared to V˙O2max.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2019 Nov;51(11):2251-2256. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000002041. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2019. PMID: 31107835 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Laukkanen JA, Kurl S, Salonen JT. Cardiorespiratory fitness and physical activity as risk predictors of future atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2002;4:468–476. - PubMed
-
- Blair SN, Kohl HW, Paffenbarger RS, Clark DG, Cooper KH, Gibbons LW. Physical fitness and all-cause mortality. JAMA. 1989;262:2395–2401. - PubMed
-
- Berry JD, Willis B, Gupta S, Barlow CE, Lakoski SG, Khera A, Rohatgi A, de Lemos JA, Haskell W, Lloyd-Jones DM. Lifetime risks for cardiovascular disease mortality by cardiorespiratory fitness levels measured at ages 45, 55, and 65 years in men: The Cooper Center Longitudinal Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57:1604–1610. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Laukkanen JA, Rauramaa R, Salonen JT, Kurl S. The predictive value of cardiorespiratory fitness combined with coronary risk evaluation and the risk of cardiovascular and all-cause death. J Intern Med. 2007;262:263–272. - PubMed
-
- Myers J, Prakash M, Froelicher V, Do D, Partington S, Atwood JE. Exercise capacity and mortality among men referred for exercise testing. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:793–801. - PubMed

