Bacterial communities in different sections of a municipal wastewater treatment plant revealed by 16S rDNA 454 pyrosequencing
- PMID: 22555912
- PMCID: PMC3586070
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-012-4082-4
Bacterial communities in different sections of a municipal wastewater treatment plant revealed by 16S rDNA 454 pyrosequencing
Abstract
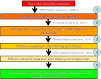
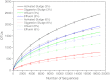
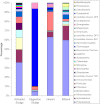
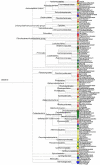
In this study, we successfully demonstrated that 454 pyrosequencing was a powerful approach for investigating the bacterial communities in the activated sludge, digestion sludge, influent, and effluent samples of a full scale wastewater treatment plant treating saline sewage. For each sample, 18,808 effective sequences were selected and utilized to do the bacterial diversity and abundance analysis. In total, 2,455, 794, 1,667, and 1,932 operational taxonomic units were obtained at 3 % distance cutoff in the activated sludge, digestion sludge, influent, and effluent samples, respectively. The corresponding most dominant classes in the four samples are Alphaproteobacteria, Thermotogae, Deltaproteobacteria, and Gammaproteobacteria. About 67 % sequences in the digestion sludge sample were found to be affiliated with the Thermotogales order. Also, these sequences were assigned into a recently proposed genus Kosmotoga by the Ribosomal Database Project classifier. In the effluent sample, we found high abundance of Mycobacterium and Vibrio, which are genera containing pathogenic bacteria. Moreover, in this study, we proposed a method to differentiate the "gene percentage" and "cell percentage" by using Ribosomal RNA Operon Copy Number Database.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tracking human sewage microbiome in a municipal wastewater treatment plant.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014 Apr;98(7):3317-26. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-5402-z. Epub 2013 Dec 5. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24305737
-
Bacterial community composition and diversity of a full-scale integrated fixed-film activated sludge system as investigated by pyrosequencing.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010 Dec;20(12):1717-23. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 21193829
-
A study of the relationship among sludge retention time, bacterial communities, and hydrolytic enzyme activities in inclined plate membrane bioreactors for the treatment of municipal wastewater.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014 Nov;98(21):9107-18. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-5914-1. Epub 2014 Jul 13. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25016344
-
Use of pyrosequencing to explore the benthic bacterial community structure in a river impacted by wastewater treatment plant discharges.Res Microbiol. 2014 Jul-Aug;165(6):468-71. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2014.04.002. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Res Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24732342
-
Bacterial communities in manures of piglets and adult pigs bred with different feeds revealed by 16S rDNA 454 pyrosequencing.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014 Mar;98(6):2657-65. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-5211-4. Epub 2013 Sep 26. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24068333
Cited by
-
Characterization of bacterial communities in wastewater with enhanced taxonomic resolution by full-length 16S rRNA sequencing.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 4;9(1):9673. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46015-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31273307 Free PMC article.
-
Seasonal Changes in Bacterial Communities Cause Foaming in a Wastewater Treatment Plant.Microb Ecol. 2016 Apr;71(3):660-71. doi: 10.1007/s00248-015-0700-x. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Microb Ecol. 2016. PMID: 26577577
-
Human health implications of clinically relevant bacteria in wastewater habitats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2013 Jun;20(6):3550-69. doi: 10.1007/s11356-013-1594-0. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23508533 Review.
-
Seasonal changes in microbial community composition in river water studied using 454-pyrosequencing.Springerplus. 2016 Apr 5;5:409. doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-2043-6. eCollection 2016. Springerplus. 2016. PMID: 27069829 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Microbial Composition of Wastewater During Treatment in a Full-Scale Plant.Curr Microbiol. 2016 Feb;72(2):128-132. doi: 10.1007/s00284-015-0924-5. Curr Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26496734
References
-
- Altschul S, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E, Lipman D. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215(3):403–410. - PubMed
-
- Claesson M, O'Sullivan O, Wang Q, Nikkila J, Marchesi J, Smidt H, De Vos W, Ross R, O'Toole P. Comparative analysis of pyrosequencing and a phylogenetic microarray for exploring microbial community structures in the human distal intestine. PLoS One. 2009;4(8):e6669. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006669. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cracraft J, Donoghue MJ. Assembling the tree of life. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2004.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

