Elementary Ca2+ signals through endothelial TRPV4 channels regulate vascular function
- PMID: 22556255
- PMCID: PMC3715993
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1216283
Elementary Ca2+ signals through endothelial TRPV4 channels regulate vascular function
Abstract
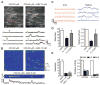
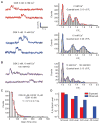
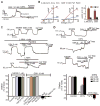
Major features of the transcellular signaling mechanism responsible for endothelium-dependent regulation of vascular smooth muscle tone are unresolved. We identified local calcium (Ca(2+)) signals ("sparklets") in the vascular endothelium of resistance arteries that represent Ca(2+) influx through single TRPV4 cation channels. Gating of individual TRPV4 channels within a four-channel cluster was cooperative, with activation of as few as three channels per cell causing maximal dilation through activation of endothelial cell intermediate (IK)- and small (SK)-conductance, Ca(2+)-sensitive potassium (K(+)) channels. Endothelial-dependent muscarinic receptor signaling also acted largely through TRPV4 sparklet-mediated stimulation of IK and SK channels to promote vasodilation. These results support the concept that Ca(2+) influx through single TRPV4 channels is leveraged by the amplifier effect of cooperative channel gating and the high Ca(2+) sensitivity of IK and SK channels to cause vasodilation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Cell biology. Superresolution subspace signaling.Science. 2012 May 4;336(6081):546-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1222540. Science. 2012. PMID: 22556238 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Saliez J, et al. Circulation. 2008;117:1065. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GM086736/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 2-P20-RR-016435-06/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL095488/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR016435/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM086736/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL098243/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK053832/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL044455/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL098243/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1P01HL095488/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37DK053832/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL044455/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

