Radio-wave heating of iron oxide nanoparticles can regulate plasma glucose in mice
- PMID: 22556257
- PMCID: PMC3646550
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1216753
Radio-wave heating of iron oxide nanoparticles can regulate plasma glucose in mice
Abstract
Medical applications of nanotechnology typically focus on drug delivery and biosensors. Here, we combine nanotechnology and bioengineering to demonstrate that nanoparticles can be used to remotely regulate protein production in vivo. We decorated a modified temperature-sensitive channel, TRPV1, with antibody-coated iron oxide nanoparticles that are heated in a low-frequency magnetic field. When local temperature rises, TRPV1 gates calcium to stimulate synthesis and release of bioengineered insulin driven by a Ca(2+)-sensitive promoter. Studying tumor xenografts expressing the bioengineered insulin gene, we show that exposure to radio waves stimulates insulin release from the tumors and lowers blood glucose in mice. We further show that cells can be engineered to synthesize genetically encoded ferritin nanoparticles and inducibly release insulin. These approaches provide a platform for using nanotechnology to activate cells.
Figures
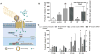
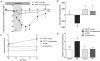
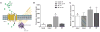
Comment in
-
Nanobiotechnology: Controlling biology by radio.Nat Methods. 2012 Jun;9(6):535. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2059. Nat Methods. 2012. PMID: 22874991 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gellhorn E, Cortell R, Feldman J. Science. 1940;92:288. - PubMed
-
- Stock G, Sturm V, Schmitt HP, Schlör KH. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1979;47:123. - PubMed
-
- McIntyre CC, Grill WM. J Neurophysiol. 2002;88:1592. - PubMed
-
- Boyden ES, Zhang F, Bamberg E, Nagel G, Deisseroth K. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:1263. - PubMed
-
- Young JH, Wang MT, Brezovich I. Electron Lett. 1980;16:358.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

