High potency zinc modulation of human P2X2 receptors and low potency zinc modulation of rat P2X2 receptors share a common molecular mechanism
- PMID: 22556417
- PMCID: PMC3381168
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.369157
High potency zinc modulation of human P2X2 receptors and low potency zinc modulation of rat P2X2 receptors share a common molecular mechanism
Abstract
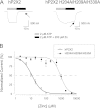
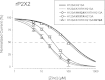
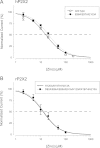
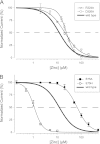
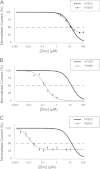
Human P2X2 receptors (hP2X2) are strongly inhibited by zinc over the range of 2-100 μM, whereas rat P2X2 receptors (rP2X2) are strongly potentiated over the same range, and then inhibited by zinc over 100 μM. However, the biological role of zinc modulation is unknown in either species. To identify candidate regions controlling zinc inhibition in hP2X2 a homology model based on the crystal structure of zebrafish P2X4.1 was made. In this model, His-204 and His-209 of one subunit were near His-330 of the adjacent subunit. Cross-linking studies confirmed that these residues are within 8 Å of each other. Simultaneous mutation of these three histidines to alanines decreased the zinc potency of hP2X2 nearly 100-fold. In rP2X2, one of these histidines is replaced by a lysine, and in a background in which zinc potentiation was eliminated, mutation of Lys-197 to histidine converted rP2X2 from low potency to high potency inhibition. We explored whether the zinc-binding site lies within the vestibules running down the central axis of the receptor. Elimination of all negatively charged residues from the upper vestibule had no effect on zinc inhibition. In contrast, mutation of several residues in the hP2X2 middle vestibule resulted in dramatic changes in the potency of zinc inhibition. In particular, the zinc potency of P206C could be reversibly shifted from extremely high (∼10 nM) to very low (>100 μM) by binding and unbinding MTSET. These results suggest that the cluster of histidines at the subunit interface controls access of zinc to its binding site.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

