Oral lymphangioma - Case reports and review of literature
- PMID: 22557912
- PMCID: PMC3341747
- DOI: 10.4103/0976-237X.94561
Oral lymphangioma - Case reports and review of literature
Abstract
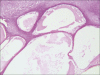
Lymphangioma is a benign hamartomatous hyperplasia of lymphatic vessels. Majority of them are superficial, but a few may extend deeply into the connective tissue. Intraoral lymphangiomas occur more frequently on the dorsum of tongue, followed by palate, buccal mucosa, gingiva, and lips. Surgical excision is the treatment of choice. The prognosis is good for most patients, although large tumors of neck/tongue may result in airway obstruction and death. This case report series discusses the clinical features, histopathology, and treatment of lymphangioma.
Keywords: Lymphangioma; lymph vessels; papule.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







References
-
- Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM. Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. 3rd Edition. Saunders Elsevier; 2009. pp. 547–49.
-
- Rajendran R, Sivapathasundaram . Shafer's Textbook of Oral Pathology. 6th edition. Elsevier; 2009. pp. 146–8.
-
- Guelmann M, Katz J. Macroglossia combined with lymphangiomaa case report. J Cli Pediatr Den. 2003;27:167–70. - PubMed
-
- Regezi, Sciubba, Jordan . Oral Pathology Clinical Pathologic Correlation. 5th edition. Elsevier; 2009. pp. 166–7.
-
- GreenBerg, Glick, Ship . Burket's Oral Medicine. 11th edition. BC Decker; 2008. pp. 139–40.

