Molecular biology of hearing
- PMID: 22558056
- PMCID: PMC3341583
- DOI: 10.3205/cto000079
Molecular biology of hearing
Abstract
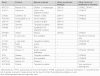
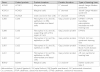
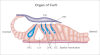
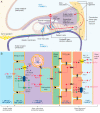
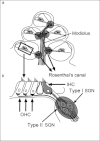
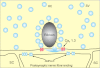
THE INNER EAR IS OUR MOST SENSITIVE SENSORY ORGAN AND CAN BE SUBDIVIDED INTO THREE FUNCTIONAL UNITS: organ of Corti, stria vascularis and spiral ganglion. The appropriate stimulus for the organ of hearing is sound, which travels through the external auditory canal to the middle ear where it is transmitted to the inner ear. The inner ear houses the hair cells, the sensory cells of hearing. The inner hair cells are capable of mechanotransduction, the transformation of mechanical force into an electrical signal, which is the basic principle of hearing. The stria vascularis generates the endocochlear potential and maintains the ionic homeostasis of the endolymph. The dendrites of the spiral ganglion form synaptic contacts with the hair cells. The spiral ganglion is composed of neurons that transmit the electrical signals from the cochlea to the central nervous system. In recent years there has been significant progress in research on the molecular basis of hearing. An increasing number of genes and proteins related to hearing are being identified and characterized. The growing knowledge of these genes contributes not only to greater appreciation of the mechanism of hearing but also to a deeper understanding of the molecular basis of hereditary hearing loss. This basic research is a prerequisite for the development of molecular diagnostics and novel therapies for hearing loss.
Keywords: cochlea; deafness; hair cell; inner ear; organ of Corti; spiral ganglion.
Figures




References
-
- Santi PA, Tsuprun VL. Cochlear microanatomy and ultrastructure. In: Jahn AF, Santos-Sacchi J, editors. Physiology of the Ear. San Diego, CA: Singular Publishing; 2001.
-
- Slepecky NB. Cochlear structure. In: Dallos P, Popper AN, Fay R, editors. The Cochlea. New York: Springer; 1996. pp. 44–129. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-0757-3_2. - DOI
-
- Boenninghaus, Lenarz . Innenohr (Labyrinth) In: Boenninghaus, Lenarz, editors. HNO. Springer Medizin Verlag; 2007. pp. 15–19.
-
- Starlinger V, Masaki K, Heller S. Auditory physiology: Inner ear. In: Gulya AJ, Minor LB, Poe DS, editors. Glasscock-Shambaugh's Surgery of the Ear. 6th ed. People's Medical Publishing House; 2010. pp. 73–83.
-
- Rhys Evans PH, Comis SD, Osborne MP, Pickles JO, Jeffries DJ. Cross-links between stereocilia in the human organ of Corti. J Laryngol Otol. 1985;99:11–19. doi: 10.1017/S0022215100096237. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0022215100096237. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

