Evaluation of SMN protein, transcript, and copy number in the biomarkers for spinal muscular atrophy (BforSMA) clinical study
- PMID: 22558076
- PMCID: PMC3338744
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033572
Evaluation of SMN protein, transcript, and copy number in the biomarkers for spinal muscular atrophy (BforSMA) clinical study
Abstract
Background: The universal presence of a gene (SMN2) nearly identical to the mutated SMN1 gene responsible for Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) has proved an enticing incentive to therapeutics development. Early disappointments from putative SMN-enhancing agent clinical trials have increased interest in improving the assessment of SMN expression in blood as an early "biomarker" of treatment effect.
Methods: A cross-sectional, single visit, multi-center design assessed SMN transcript and protein in 108 SMA and 22 age and gender-matched healthy control subjects, while motor function was assessed by the Modified Hammersmith Functional Motor Scale (MHFMS). Enrollment selectively targeted a broad range of SMA subjects that would permit maximum power to distinguish the relative influence of SMN2 copy number, SMA type, present motor function, and age.
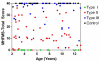
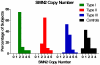
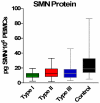
Results: SMN2 copy number and levels of full-length SMN2 transcripts correlated with SMA type, and like SMN protein levels, were lower in SMA subjects compared to controls. No measure of SMN expression correlated strongly with MHFMS. A key finding is that SMN2 copy number, levels of transcript and protein showed no correlation with each other.
Conclusion: This is a prospective study that uses the most advanced techniques of SMN transcript and protein measurement in a large selectively-recruited cohort of individuals with SMA. There is a relationship between measures of SMN expression in blood and SMA type, but not a strong correlation to motor function as measured by the MHFMS. Low SMN transcript and protein levels in the SMA subjects relative to controls suggest that these measures of SMN in accessible tissues may be amenable to an "early look" for target engagement in clinical trials of putative SMN-enhancing agents. Full length SMN transcript abundance may provide insight into the molecular mechanism of phenotypic variation as a function of SMN2 copy number.
Trial registry: Clinicaltrials.gov NCT00756821.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Mailman MD, Heinz JW, Papp AC, Snyder PJ, Sedra MS, et al. Molecular analysis of spinal muscular atrophy and modification of the phenotype by SMN2. Genet Med. 2002;4:20–26. - PubMed
-
- Lefebvre S, Burlet P, Viollet L, Bertrandy S, Huber C, et al. A novel association of the SMN protein with two major non-ribosomal nucleolar proteins and its implication in spinal muscular atrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 2002;11:1017–1027. - PubMed
-
- Owen N, Doe CL, Mellor J, Davies KE. Characterization of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe orthologue of the human survival motor neuron (SMN) protein. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9:675–684. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- NIH 1 UL1RR024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR 025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 1UL1-RR024979/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- NIH UL1-RR-024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 1KL2-RR024980/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR025764/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025764/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR025755/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR002172/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR024980/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR011234/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025755/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 1TL1-RR024981/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- MO1-RR02172/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 RR024981/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD069045/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024979/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

