Overexpression of angiopoietin-1 increases CD133+/c-kit+ cells and reduces myocardial apoptosis in db/db mouse infarcted hearts
- PMID: 22558265
- PMCID: PMC3338852
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035905
Overexpression of angiopoietin-1 increases CD133+/c-kit+ cells and reduces myocardial apoptosis in db/db mouse infarcted hearts
Abstract
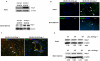
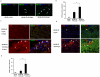
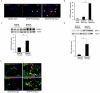
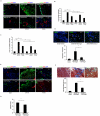
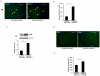
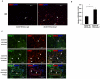
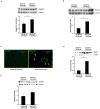
Hematopoietic progenitor CD133(+)/c-kit(+) cells have been shown to be involved in myocardial healing following myocardial infarction (MI). Previously we demonstrated that angiopoietin-1(Ang-1) is beneficial in the repair of diabetic infarcted hearts. We now investigate whether Ang-1 affects CD133(+)/c-kit(+) cell recruitment to the infarcted myocardium thereby mediating cardiac repair in type II (db/db) diabetic mice. db/db mice were administered either adenovirus Ang-1 (Ad-Ang-1) or Ad-β-gal systemically immediately after ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD). Overexpression of Ang-1 resulted in a significant increase in CXCR-4/SDF-1α expression and promoted CD133(+)/c-kit(+), CD133(+)/CXCR-4(+) and CD133(+)/SDF-1α(+) cell recruitment into ischemic hearts. Overexpression of Ang-1 led to significant increases in number of CD31(+) and smooth muscle-like cells and VEGF expression in bone marrow (BM). This was accompanied by significant decreases in cardiac apoptosis and fibrosis and an increase in myocardial capillary density. Ang-1 also upregulated Jagged-1, Notch3 and apelin expression followed by increases in arteriole formation in the infarcted myocardium. Furthermore, overexpression of Ang-1 resulted in a significant improvement of cardiac functional recovery after 14 days of ischemia. Our data strongly suggest that Ang-1 attenuates cardiac apoptosis and promotes cardiac repair by a mechanism involving in promoting CD133(+)/c-kit(+) cells and angiogenesis in diabetic db/db mouse infarcted hearts.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
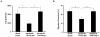
Similar articles
-
Apelin-13 increases myocardial progenitor cells and improves repair postmyocardial infarction.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012 Sep 1;303(5):H605-18. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00366.2012. Epub 2012 Jun 29. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22752632 Free PMC article.
-
Post-infarct treatment with [Pyr(1)]apelin-13 improves myocardial function by increasing neovascularization and overexpression of angiogenic growth factors in rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Aug 15;761:101-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.04.034. Epub 2015 May 1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25936512
-
Myocardial injection of apelin-overexpressing bone marrow cells improves cardiac repair via upregulation of Sirt3 after myocardial infarction.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 6;8(9):e71041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071041. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24039710 Free PMC article.
-
SDF-1α as a therapeutic stem cell homing factor in myocardial infarction.Pharmacol Ther. 2011 Jan;129(1):97-108. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.09.011. Epub 2010 Oct 20. Pharmacol Ther. 2011. PMID: 20965212 Review.
-
Competitive signaling and cellular communications in myocardial infarction response.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jan 16;52(1):129. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10236-5. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39820809 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiac regeneration and diabetes.Regen Med Res. 2014 Jan 3;2(1):1. doi: 10.1186/2050-490X-2-1. eCollection 2014 Dec. Regen Med Res. 2014. PMID: 25984329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic Analysis of Estrogen-Mediated Enhancement of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Induced Angiogenesis In Vivo.Cells. 2021 Aug 24;10(9):2181. doi: 10.3390/cells10092181. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34571830 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism of all-trans retinoic acid in the regulation of apelin expression in vascular endothelial cells.Biosci Rep. 2017 Dec 12;37(6):BSR20170684. doi: 10.1042/BSR20170684. Print 2017 Dec 22. Biosci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29070519 Free PMC article.
-
Angiopoietin-1 improves endothelial progenitor cell-dependent neovascularization in diabetic wounds.Surgery. 2015 Sep;158(3):846-56. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2015.06.034. Surgery. 2015. PMID: 26266763 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic inhalation of e-cigarette vapor containing nicotine disrupts airway barrier function and induces systemic inflammation and multiorgan fibrosis in mice.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018 Jun 1;314(6):R834-R847. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00270.2017. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29384700 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Suri C, Jones PF, Patan S, Bartunkova S, Maisonpierre PC, et al. Requisite role of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, during embryonic angiogenesis. Cell. 1996;87:1171–1180. - PubMed
-
- Papapetropoulos A, Fulton D, Mahboubi K, Kalb RG, O’Connor DS, et al. Angiopoietin-1 inhibits endothelial cell apoptosis via the Akt/survivin pathway. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:9102–9105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

