Role of advanced glycation end products in cardiovascular disease
- PMID: 22558488
- PMCID: PMC3342583
- DOI: 10.4330/wjc.v4.i4.90
Role of advanced glycation end products in cardiovascular disease
Abstract
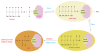
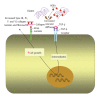
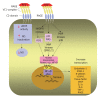
Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) are produced through the non enzymatic glycation and oxidation of proteins, lipids and nucleic acids. Enhanced formation of AGEs occurs particularly in conditions associated with hyperglycaemia such as diabetes mellitus (DM). AGEs are believed to have a key role in the development and progression of cardiovascular disease in patients with DM through the modification of the structure, function and mechanical properties of tissues through crosslinking intracellular as well as extracellular matrix proteins and through modulating cellular processes through binding to cell surface receptors [receptor for AGEs (RAGE)]. A number of studies have shown a correlation between serum AGE levels and the development and severity of heart failure (HF). Moreover, some studies have suggested that therapies targeted against AGEs may have therapeutic potential in patients with HF. The purpose of this review is to discuss the role of AGEs in cardiovascular disease and in particular in heart failure, focussing on both cellular mechanisms of action as well as highlighting how targeting AGEs may represent a novel therapeutic strategy in the treatment of HF.
Keywords: Advanced glycation end products; Atherosclerosis; Cardiovascular disease; Diabetes; Heart failure.
Figures

References
-
- Thorpe SR, Baynes JW. Maillard reaction products in tissue proteins: new products and new perspectives. Amino Acids. 2003;25:275–281. - PubMed
-
- Brownlee M, Cerami A, Vlassara H. Advanced glycosylation end products in tissue and the biochemical basis of diabetic complications. N Engl J Med. 1988;318:1315–1321. - PubMed
-
- Sell DR, Lapolla A, Odetti P, Fogarty J, Monnier VM. Pentosidine formation in skin correlates with severity of complications in individuals with long-standing IDDM. Diabetes. 1992;41:1286–1292. - PubMed
-
- Bidasee KR, Nallani K, Yu Y, Cocklin RR, Zhang Y, Wang M, Dincer UD, Besch HR. Chronic diabetes increases advanced glycation end products on cardiac ryanodine receptors/calcium-release channels. Diabetes. 2003;52:1825–1836. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

