Tavaxy: integrating Taverna and Galaxy workflows with cloud computing support
- PMID: 22559942
- PMCID: PMC3583125
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-77
Tavaxy: integrating Taverna and Galaxy workflows with cloud computing support
Abstract
Background: Over the past decade the workflow system paradigm has evolved as an efficient and user-friendly approach for developing complex bioinformatics applications. Two popular workflow systems that have gained acceptance by the bioinformatics community are Taverna and Galaxy. Each system has a large user-base and supports an ever-growing repository of application workflows. However, workflows developed for one system cannot be imported and executed easily on the other. The lack of interoperability is due to differences in the models of computation, workflow languages, and architectures of both systems. This lack of interoperability limits sharing of workflows between the user communities and leads to duplication of development efforts.
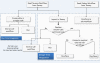
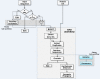
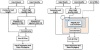
Results: In this paper, we present Tavaxy, a stand-alone system for creating and executing workflows based on using an extensible set of re-usable workflow patterns. Tavaxy offers a set of new features that simplify and enhance the development of sequence analysis applications: It allows the integration of existing Taverna and Galaxy workflows in a single environment, and supports the use of cloud computing capabilities. The integration of existing Taverna and Galaxy workflows is supported seamlessly at both run-time and design-time levels, based on the concepts of hierarchical workflows and workflow patterns. The use of cloud computing in Tavaxy is flexible, where the users can either instantiate the whole system on the cloud, or delegate the execution of certain sub-workflows to the cloud infrastructure.
Conclusions: Tavaxy reduces the workflow development cycle by introducing the use of workflow patterns to simplify workflow creation. It enables the re-use and integration of existing (sub-) workflows from Taverna and Galaxy, and allows the creation of hybrid workflows. Its additional features exploit recent advances in high performance cloud computing to cope with the increasing data size and complexity of analysis.The system can be accessed either through a cloud-enabled web-interface or downloaded and installed to run within the user's local environment. All resources related to Tavaxy are available at http://www.tavaxy.org.
Figures







References
-
- Sana M, Iascone M, Marchetti D, Palatini J, Galasso M, Volinia S. GAMES identifies and annotates mutations in next-generation sequencing projects. Bioinformics. 2010;27:9–13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

