Characterization of metabolic changes associated with the functional development of 3D engineered tissues by non-invasive, dynamic measurement of individual cell redox ratios
- PMID: 22560200
- PMCID: PMC3387752
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.04.024
Characterization of metabolic changes associated with the functional development of 3D engineered tissues by non-invasive, dynamic measurement of individual cell redox ratios
Abstract
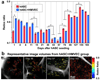
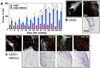
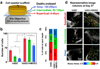
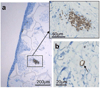
Non-invasive approaches to assess tissue function could improve significantly current methods to diagnose diseases and optimize engineered tissues. In this study, we describe a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy approach that relies entirely on endogenous fluorophores to dynamically quantify functional metabolic readouts from individual cells within three-dimensional engineered tissues undergoing adipogenic differentiation over six months. Specifically, we employ an automated approach to analyze 3D image volumes and extract a redox ratio of metabolic cofactors. We identify a decrease in redox ratio over the first two months of culture that is associated with stem cell differentiation and lipogenesis. In addition, we demonstrate that the presence of endothelial cells facilitate greater cell numbers deeper within the engineered tissues. Since traditional assessments of engineered tissue structure and function are destructive and logistically intensive, this non-destructive, label-free approach offers a potentially powerful high-content characterization tool for optimizing tissue engineering protocols and assessing engineered tissue implants.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Coleman SR. Structural fat grafting: more than a permanent filler. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;118:108S–120S. - PubMed
-
- Li WJ, Tuli R, Okafor C, Derfoul A, Danielson KG, Hall DJ, et al. A three-dimensional nanofibrous scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering using human mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2005;26:599–609. - PubMed
-
- Kim HJ, Kim UJ, Vunjak-Novakovic G, Min BH, Kaplan DL. Influence of macroporous protein scaffolds on bone tissue engineering from bone marrow stem cells. Biomaterials. 2005;26:4442–4452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

