Interplay between lipids and branched-chain amino acids in development of insulin resistance
- PMID: 22560213
- PMCID: PMC3695706
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.01.024
Interplay between lipids and branched-chain amino acids in development of insulin resistance
Abstract
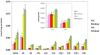
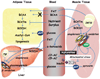
Fatty acids (FA) and FA-derived metabolites have long been implicated in the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Surprisingly, application of metabolomics technologies has revealed that branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) and related metabolites are more strongly associated with insulin resistance than many common lipid species. Moreover, the BCAA-related signature is predictive of incident diabetes and intervention outcomes and uniquely responsive to therapeutic interventions. Nevertheless, in animal feeding studies, BCAA supplementation requires the background of a high-fat diet to promote insulin resistance. This Perspective develops a model to explain how lipids and BCAA may synergize to promote metabolic diseases.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Boucher A, Lu D, Burgess S, Telemaque-Potts S, Jensen M, Mulder H, Wang M-Y, Unger RH, Sherry AD, Newgard CB. Mechanism of lipid-induced impairment of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and its reversal by an analogue of malate. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:27263–27271. - PubMed
-
- Clifton P. Diabetes: treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus with bariatric surgery. Nature Rev. Endocrinol. 2010;6:191–193. - PubMed
-
- Cota D, Proulx K, Smith KA, Kozma SC, Thomas G, Woods SC, Seeley RJ. Hypothalamic mTOR signaling regulates food intake. Science. 2006;312:927–930. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

