Increased hepatic synthesis and dysregulation of cholesterol metabolism is associated with the severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 22560219
- PMCID: PMC3361911
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.004
Increased hepatic synthesis and dysregulation of cholesterol metabolism is associated with the severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with increased cardiovascular and liver-related mortality. NAFLD is characterized by both triglyceride and free cholesterol (FC) accumulation without a corresponding increment in cholesterol esters. The aim of this study was to evaluate the expression of cholesterol metabolic genes in NAFLD and relate these to disease phenotype. NAFLD was associated with increased SREBP-2 maturation, HMG CoA reductase (HMGCR) expression and decreased phosphorylation of HMGCR. Cholesterol synthesis was increased as measured by the circulating desmosterol:cholesterol ratio. miR-34a, a microRNA increased in NAFLD, inhibited sirtuin-1 with downstream dephosphorylation of AMP kinase and HMGCR. Cholesterol ester hydrolase was increased while ACAT-2 remained unchanged. LDL receptor expression was significantly decreased and similar in NAFLD subjects on or off statins. HMGCR expression was correlated with FC, histologic severity of NAFLD and LDL-cholesterol. These data demonstrate dysregulated cholesterol metabolism in NAFLD which may contribute to disease severity and cardiovascular risks.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
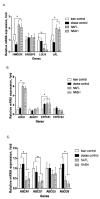
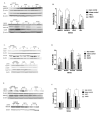

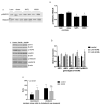
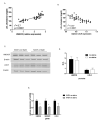
Comment in
-
Cholesterol and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: renewed focus on an old villain.Hepatology. 2012 Nov;56(5):1995-8. doi: 10.1002/hep.26088. Hepatology. 2012. PMID: 23115010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams LA, Sanderson S, Lindor KD, Angulo P. The histological course of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a longitudinal study of 103 patients with sequential liver biopsies. J Hepatol. 2005;42:132–138. - PubMed
-
- Beg ZH, Stonik JA, Brewer HB., Jr. Phosphorylation of hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase and modulation of its enzymic activity by calcium-activated and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1985;260:1682–1687. - PubMed
-
- Beg ZH, Stonik JA, Brewer HB., Jr. Modulation of the enzymic activity of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase by multiple kinase systems involving reversible phosphorylation: a review. Metabolism: clinical and experimental. 1987;36:900–917. - PubMed
-
- Bloomston M, Frankel WL, Petrocca F, Volinia S, Alder H, Hagan JP, Liu CG, Bhatt D, Taccioli C, Croce CM. MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA. 2007;297:1901–1908. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

