SIRT1 is required for AMPK activation and the beneficial effects of resveratrol on mitochondrial function
- PMID: 22560220
- PMCID: PMC3545644
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.003
SIRT1 is required for AMPK activation and the beneficial effects of resveratrol on mitochondrial function
Abstract
Resveratrol induces mitochondrial biogenesis and protects against metabolic decline, but whether SIRT1 mediates these benefits is the subject of debate. To circumvent the developmental defects of germline SIRT1 knockouts, we have developed an inducible system that permits whole-body deletion of SIRT1 in adult mice. Mice treated with a moderate dose of resveratrol showed increased mitochondrial biogenesis and function, AMPK activation, and increased NAD(+) levels in skeletal muscle, whereas SIRT1 knockouts displayed none of these benefits. A mouse overexpressing SIRT1 mimicked these effects. A high dose of resveratrol activated AMPK in a SIRT1-independent manner, demonstrating that resveratrol dosage is a critical factor. Importantly, at both doses of resveratrol no improvements in mitochondrial function were observed in animals lacking SIRT1. Together these data indicate that SIRT1 plays an essential role in the ability of moderate doses of resveratrol to stimulate AMPK and improve mitochondrial function both in vitro and in vivo.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

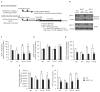



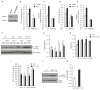
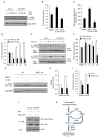
Comment in
-
Fortifying the link between SIRT1, resveratrol, and mitochondrial function.Cell Metab. 2012 May 2;15(5):566-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.016. Cell Metab. 2012. PMID: 22560207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal B, Baur JA. Resveratrol and life extension. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011;1215:138–143. - PubMed
-
- Barger JL, Kayo T, Pugh TD, Prolla TA, Weindruch R. Short-term consumption of a resveratrol-containing nutraceutical mixture mimics gene expression of long-term caloric restriction in mouse heart. Exp Gerontol. 2008a;43:859–866. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

