Pediatric vasculitis
- PMID: 22560577
- PMCID: PMC3348547
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pcl.2012.03.013
Pediatric vasculitis
Abstract
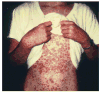
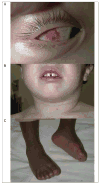
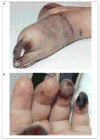
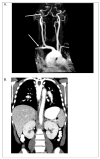
Childhood vasculitis is a challenging and complex group of conditions that are multisystem in nature and often require integrated care from multiple subspecialties, including rheumatology, dermatology, cardiology, nephrology, neurology, and gastroenterology. Vasculitis is defined as the presence of inflammation in the blood vessel wall. The site of vessel involvement, size of the affected vessels, extent of vascular injury, and underlying pathology determine the disease phenotype and severity. This article explores the classification and general features of pediatric vasculitis, as well as the clinical presentation, diagnostic evaluation, and therapeutic options for the most common vasculitides.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Gardner-Medwin JM, Dolezalova P, Cummins C, Southwood TR. Incidence of Henoch-Schonlein purpura, Kawasaki disease, and rare vasculitides in children of different ethnic origins. Lancet. 2002;360:1197–202. - PubMed
-
- Natter M, Winsor J, Fox K, et al. Rheumatology ACo. The Childhood Arthritis & Rheumatology Research Alliance Network Registry: Demographics and Characteristics of the Initial 6-Month Cohort. Pediatric Rheumatology Symposium (PRSYM); Miami, Florida. 2011. pp. 43–4.
-
- Denardo BA, Tucker LB, Miller LC, Szer IS, Schaller JG. Demography of a regional pediatric rheumatology patient population. Affiliated Children’s Arthritis Centers of New England. J Rheumatol. 1994;21:1553–61. - PubMed
-
- Malleson PN, Fung MY, Rosenberg AM. The incidence of pediatric rheumatic diseases: results from the Canadian Pediatric Rheumatology Association Disease Registry. The Journal of rheumatology. 1996;23:1981–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

